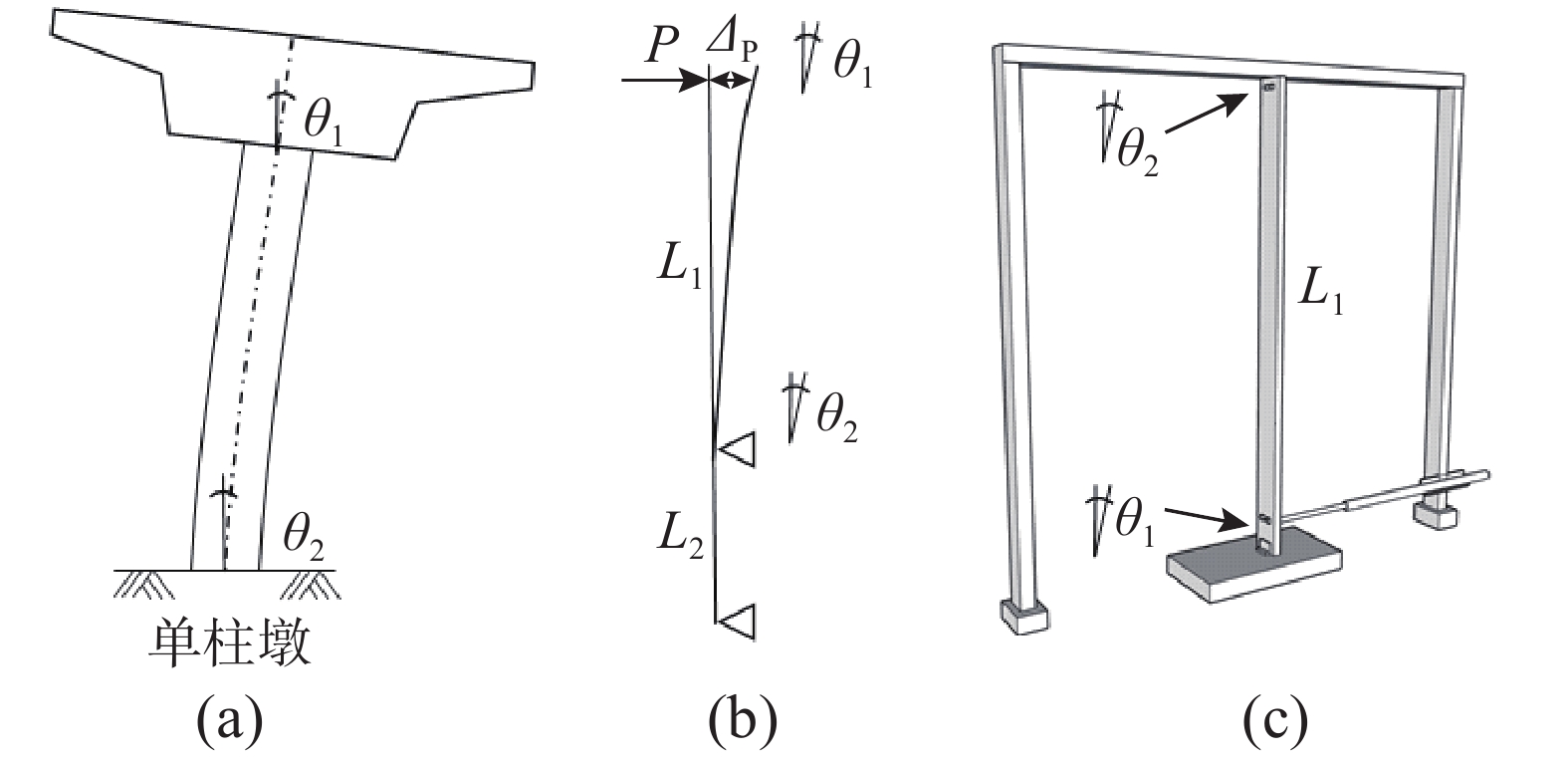
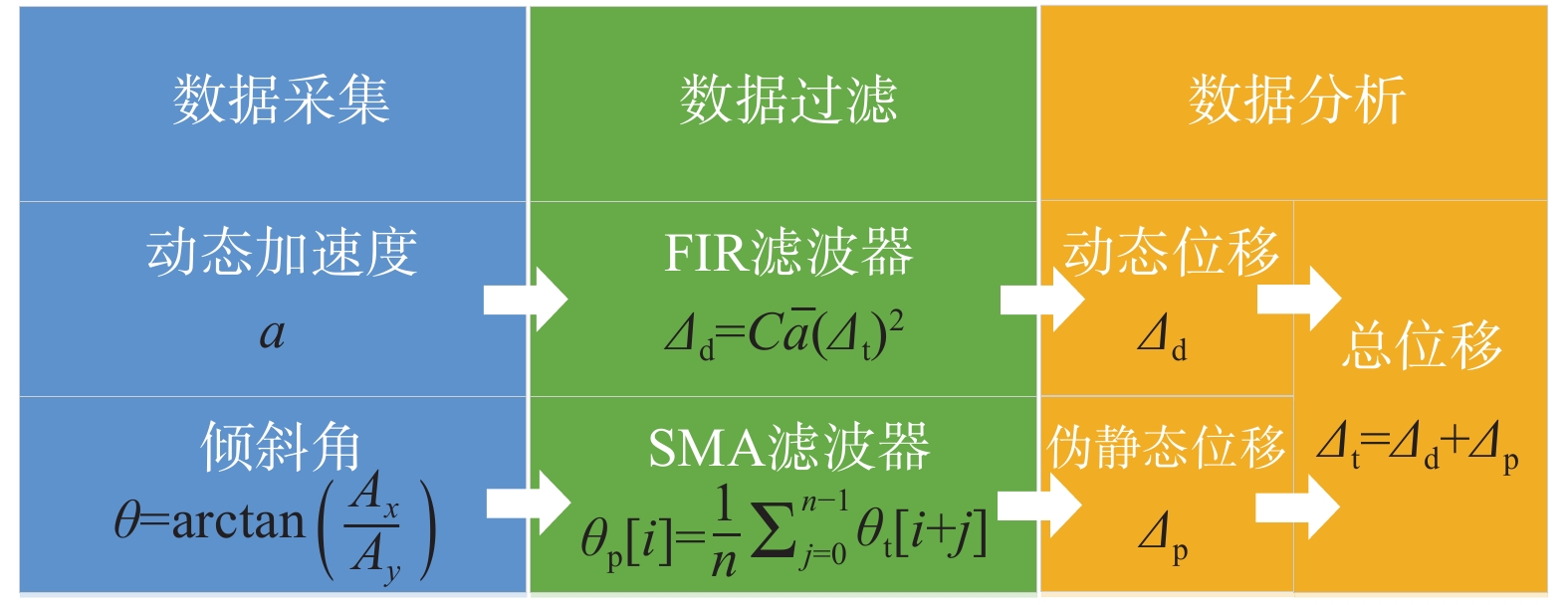
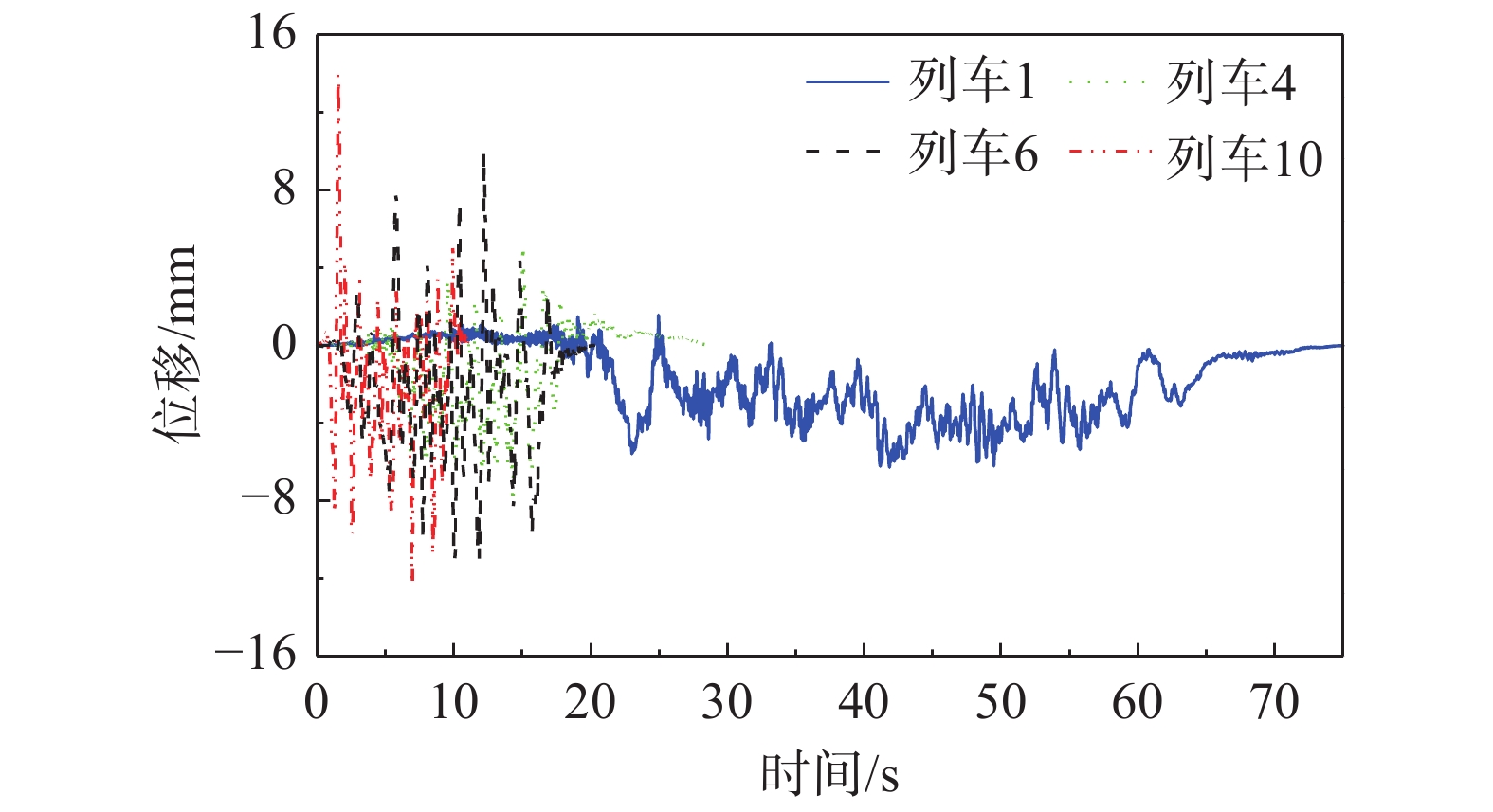
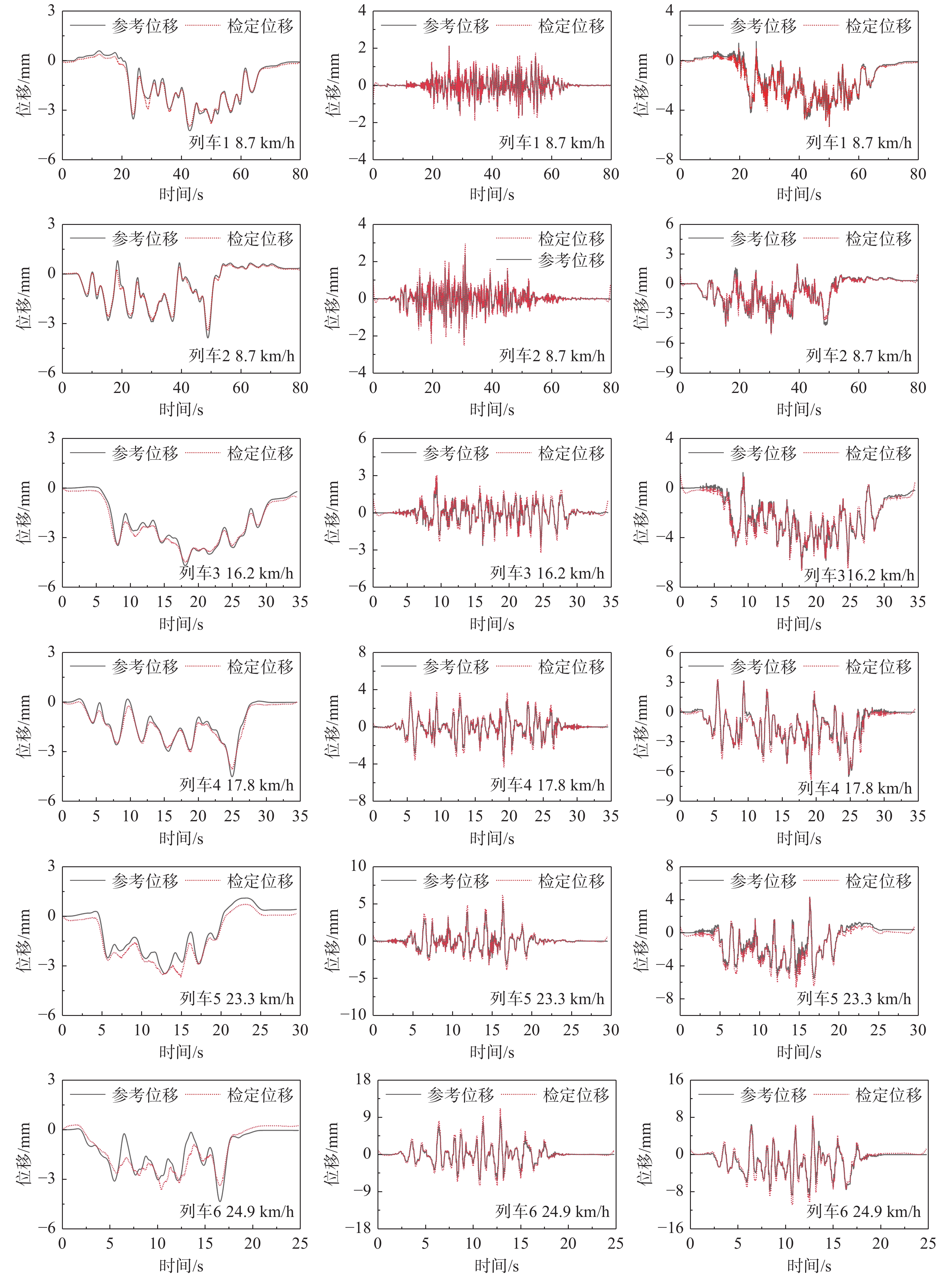
A NOVEL ACCELEROMETER-BASED METHOD FOR ESTIMATING THE TRANSVERSE DISPLACEMENT OF LIGHT PIER RAILROAD BRIDGES AND SHAKING TABLE TEST VERIFICATION
-
摘要: 截至2019年,全国铁路完成货物发送量43.89亿吨,且货运量年增长率保持在9%~10%。既有线路有很大比例的早期建设的轻型桥墩桥梁,由于其横向刚度较弱,在运营过程中常常出现横向位移较大的现象。随着既有线提速及货运量的增加,这一现象愈加明显。铁路运营期间,为防止列车脱轨,对于该类桥梁的位移变形的要求较高。因此需要一种能够适应恶劣的环境条件,可以实时持续可靠地监测桥梁位移的方法。当前测量桥梁位移的方法,通常基于昂贵的设备和复杂的模型,并且局限于良好的天气条件并不能满足在有限的成本下对桥梁进行持续高效的维护。该文提出一种基于加速度传感器的检定轻墩铁路桥梁横向位移的监测方法。其特点是,依靠低成本易操作的加速度传感器对桥梁高频动态位移和低频伪静态位移进行持续准确的监测检定,而不需要依靠良好的天气环境和架设条件。该研究设计一种巧妙的振动台试验,通过一系列的试验对该方法进行了验证。试验结果表明:加速度传感器能够准确的检定位移,与线性随动位移计相比,最大峰值误差只有11.80%,最大均值位移误差只有8.05%。Abstract: As of 2019, the nation's railroads have delivered a total of 4.38 billion tons of freight. A significant number of current piers are light piers built earlier, and are often deflected due to their limited lateral stiffness. The deflection of piers is getting increasingly evident as the line speeds up and freight increases. On the other hand, the railroad requires a high deformity of train tracks to avoid derailment. Hence, a method is in need that can monitor the track displacement in harsh environments timely and continuously. Current methods depend on costly machines and accurate models which are available only under good weather conditions. It presents a technique to track the lateral movement of light piers with accelerometers. It utilizes low-cost and easy-to-mount accelerometers for persistent and reliable detection of high-dynamic and low-frequency pseudo-static displacements. A novel shaking table is built and the concept is proven by numerical experiments. Compared with the linear follower displacement meter, the peak error is 11.80% and the mean error is 8.05%.
-
-
表 1 Model 3711E1110G直流加速度计性能参数
Table 1 Model 3711E1110G DC accelerometer performance parameters
性能 描述 灵敏度 (±5%) 200 mV/g (20.4 mV/(m/s2)) 测量范围 ±10 g (±98.1 m/s2 峰值) 宽带分辨率 (0.5 Hz~100 Hz) 0.2 mg均方根加速度
(0.002 m/s2均方根加速度)温度范围 (工作温度范围) −65℉ ~ +250℉ (−54.0 ℃ ~ +121 ℃) 频率范围 (±3 dB) 0 Hz~1000 Hz 电源接口 4针 表 2 线性可变差动变压器(LVDT)性能参数
Table 2 Linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) performance parameters
性能 描述 电压 14 V~26 V, 30 mA 输出 0 V~10 V (负满量程) 输出荷载 2 k Ohms 输出波动 30 mV (峰值对峰值) 电输出带宽 200 Hz 输出阻抗 2 Ohms 温度系数 ±0.017% F.S./ ℉ (正常环境) 工作温度范围 −40℉~158℉ 电终端 6.6 ft (电缆总长) 表 3 10组位移时程数据
Table 3 10 sets of displacement time history data
列车 方向 时间/s 正总峰值
位移/mm负总峰值
位移/mm正动峰值
位移/mm负动峰值
位移/mm正静峰值
位移/mm负静峰值
位移/mm列车速度/
(km/h)1 SB 74.23 1.550 −6.272 3.975 −3.901 0.520 −4.295 8.7 2 NB 73.07 2.627 −6.509 3.612 −3.549 0.526 −2.967 8.7 3 SB 33.75 1.300 −8.321 4.141 −3.805 0.009 −5.134 16.2 4 NB 32.94 4.071 −8.207 5.140 −5.046 0.058 −4.254 17.8 5 SB 24.62 4.968 −7.132 6.423 −4.184 1.323 −4.302 23.3 6 NB 19.86 9.851 −11.055 11.406 −7.772 0.018 −5.356 24.9 7 SB 28.22 4.870 −8.114 6.779 −5.526 0.938 −3.106 33.9 8 NB 15.91 13.698 −13.378 13.310 −9.780 0.445 −5.603 31.1 9 SB 13.36 5.656 −12.441 5.892 −5.093 1.164 −7.942 41.5 10 NB 11.29 13.925 −12.320 10.467 −7.089 3.880 −5.089 41.0 表 4 10组检定位移时程曲线峰值位移误差E1数据
Table 4 Peak displacement error E1 of 10 sets of estimated displacement time history curves
E1/(%) 1组 2组 3组 4组 5组 6组 7组 8组 9组 10组 平均 动态位移 0.50 26.61 14.74 15.55 15.72 22.07 13.08 20.11 15.05 19.60 16.30 伪静态位移 6.22 11.78 3.67 9.82 6.37 16.37 4.70 14.68 3.59 9.50 8.67 总位移 2.41 4.53 2.61 5.08 8.20 11.80 9.44 6.67 3.71 0.08 5.45 表 5 10组检定位移时程曲线均方根位移误差E2数据
Table 5 RMS displacement error E2 of 10 group estimated displacement time-course curve
E2/(%) 1组 2组 3组 4组 5组 6组 7组 8组 9组 10组 平均 动态位移 4.89 5.39 6.81 5.96 4.59 5.41 5.23 5.26 6.57 5.35 5.55 伪静态位移 3.87 3.98 4.37 4.53 11.37 11.34 18.18 14.42 7.45 19.60 9.91 总位移 3.61 3.99 3.82 4.30 7.85 6.56 8.05 6.43 4.38 5.71 5.47 -
[1] 张文学, 李建中, 苏木标, 等. 轻型铁路桥墩横向振动问题研究[J]. 工程力学, 2006(8): 122 − 126, 154. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2006.08.023 Zhang Wenxue, Li Jianzhong, Su Mubiao, et al. Transverse vibration of lightweight railway-bridge pier [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2006(8): 122 − 126, 154. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2006.08.023
[2] Chen L, Jiang L, Li R, et al. A feasible vibration measurement and active control method of reinforced concrete lightweight pier railway bridges for heavy-haul monorail trains [J]. European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering, 2019. doi: 10.1080/19648189.2019.1663267
[3] Wang H, Mao J X, Spencer Jr B F. A monitoring-based approach for evaluating dynamic responses of riding vehicle on long-span bridge under strong winds [J]. Engineering Structures, 2019, 189: 35 − 47. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2019.03.075
[4] Xu Y, Brownjohn J M W, Huseynov F. Accurate deformation monitoring on bridge structures using a cost-effective sensing system combined with a camera and accelerometers: Case study [J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2019, 24(1): 05018014. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0001330
[5] Lin W, Butler L J, Elshafie M Z E B, et al. Performance assessment of a newly constructed skewed half-through railway bridge using integrated sensing [J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2019, 24(1): 04018107. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0001334
[6] 夏禾, 张楠, 高日, 黄绚晔. 铁路桥梁与高速列车的动力试验研究[J]. 工程力学, 2007(9): 166 − 172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2007.09.026 Xia He, Zhang Nan, Gao Ri, Huang Xuanye. Experimental study on a railway bridge and high speed trains [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2007(9): 166 − 172. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2007.09.026
[7] 李小珍, 邱晓为, 刘德军, 秦羽. 时速400 km/h铁路常用跨度预应力混凝土简支梁竖向基频限值研究[J]. 工程力学, 2018, 35(5): 204 − 213. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2017.04.0273 Li Xiaozhen, Qiu Xiaowei, Liu Dejun, Qin Yu. Research on the basic frequency limit of railway common span prestressed concrete simply supported beam with 400 km/h [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2018, 35(5): 204 − 213. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2017.04.0273
[8] 蒋丽忠, 邵光强, 王辉, 姜静静. 高速铁路圆端形空心桥墩抗震性能试验研究[J]. 工程力学, 2014, 31(3): 72 − 82. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2013.01.0111 Jiang Lizhong, Shao Guangqiang, Wang Hui, Jiang Jingjing. Experimental study on seismic performance of hollow piers with rounded rectangular cross section in high-speed railways [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2014, 31(3): 72 − 82. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2013.01.0111
[9] 郑秋怡, 周广东, 刘定坤. 基于长短时记忆神经网络的大跨拱桥温度-位移相关模型建立方法[J]. 工程力学, 2021, 38(4): 68 − 79. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2020.05.0323 Zheng Qiuyi, Zhou Guangdong, Liu Dingkun. Method of modeling temperature-displacement correlation for long-span arch bridges based on long short-term memory neural networks [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2021, 38(4): 68 − 79. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2020.05.0323
[10] Stiros S C, Psimoulis P A. Response of a historical short-span railway bridge to passing trains: 3-D deflections and dominant frequencies derived from Robotic Total Station (RTS) measurements [J]. Engineering Structures, 2012, 45: 362 − 371. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2012.06.029
[11] Psimoulis P A, Stiros S C. Measuring Deflections of a Short-Span Railway Bridge Using a Robotic Total Station [J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2013, 18(2): 182 − 185. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0000334
[12] Garg P, Moreu F, Ozdagli A, et al. Noncontact dynamic displacement measurement of structures using a moving laser Doppler vibrometer [J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2019, 24(9): 04019089. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0001472
[13] Gaxiola-Camacho J R, Vazquez-Ontiveros J R, Guzman-Acevedo G M, et al. Real-Time Probabilistic Structural Evaluation of Bridges Using Dynamic Displacements Extracted via GPS Technology [J]. Journal of Surveying Engineering, 2021, 147(2): 04021002. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)SU.1943-5428.0000350
[14] Zhao H W, Ding Y L, Nagarajaiah S, et al. Behavior analysis and early warning of girder deflections of a steel-truss arch railway bridge under the effects of temperature and trains: case study [J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2019, 24(1): 05018013. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0001327
[15] Ribeiro D, Calcada R, Ferreira J, et al. Non-contact measurement of the dynamic displacement of railway bridges using an advanced video-based system [J]. Engineering Structures, 2014, 75: 164 − 180. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2014.04.051
[16] Wang X, Wittich C E, Hutchinson T C, et al. Methodology and validation of UAV-based video analysis approach for tracking earthquake-induced building displacements [J]. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 2020, 34(6): 04020045. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)CP.1943-5487.0000928
[17] Sun L, Shang Z, Xia Y, et al. Review of bridge structural health monitoring aided by big data and artificial intelligence: From condition assessment to damage detection [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2020, 146(5): 04020073. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0002535
[18] Lin J J, Ibrahim A, Sarwade S, et al. Bridge inspection with aerial robots: Automating the entire pipeline of visual data capture, 3D mapping, defect detection, analysis, and reporting [J]. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 2021, 35(2): 04020064. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)CP.1943-5487.0000954
[19] Moreu F, Li J, Jo H, et al. Reference-free displacements for condition assessment of tmber railroad bridges [J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2016, 21(2): 04015052. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0000805
[20] Lee C H, Kim C W, Kawatani M, et al. Dynamic response analysis of monorail bridges under moving trains and riding comfort of trains [J]. Engineering Structures, 2005, 27(14): 1999-2013.
[21] Dias R. Dynamic behaviour of high speed railway bridges. Vehicles lateral dynamic behaviour [D]. Madrid: Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, 2007.
[22] Hester D, Brownjohn J, Bocian M, et al. Low cost bridge load test: Calculating bridge displacement from acceleration for load assessment calculations [J]. Engineering Structures, 2017, 143: 358 − 374. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2017.04.021
[23] Lee H S, Hong Y H, Park H W. Design of an FIR filter for the displacement reconstruction using measured acceleration in low-frequency dominant structures[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2010, 82(4): 403-434.
[24] Hansen P C. Rank-deficient and discrete ill-posed problems: Numerical aspects of linear inversion [M]. Philadelphia, USA: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 1998.
[25] Park H W, Shin S, Lee H S. Determination of an optimal regularization factor in system identification with Tikhonov regularization for linear elastic continua [J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2010, 51(10): 1211 − 1230.
[26] Fisher Christopher J. Using an accelerometer for inclination sensing [J]. Application note, AN-1057, Analog Devices, 2010: 1 − 8.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 林子力,许芸熙. 地震作用下的桥梁位移响应倾斜摄影监测方法. 华南地震. 2025(01): 132-137 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 文波. 基于振动监测的水利工程边坡爆破开挖风险评估. 水利科技与经济. 2024(07): 74-78+98 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)



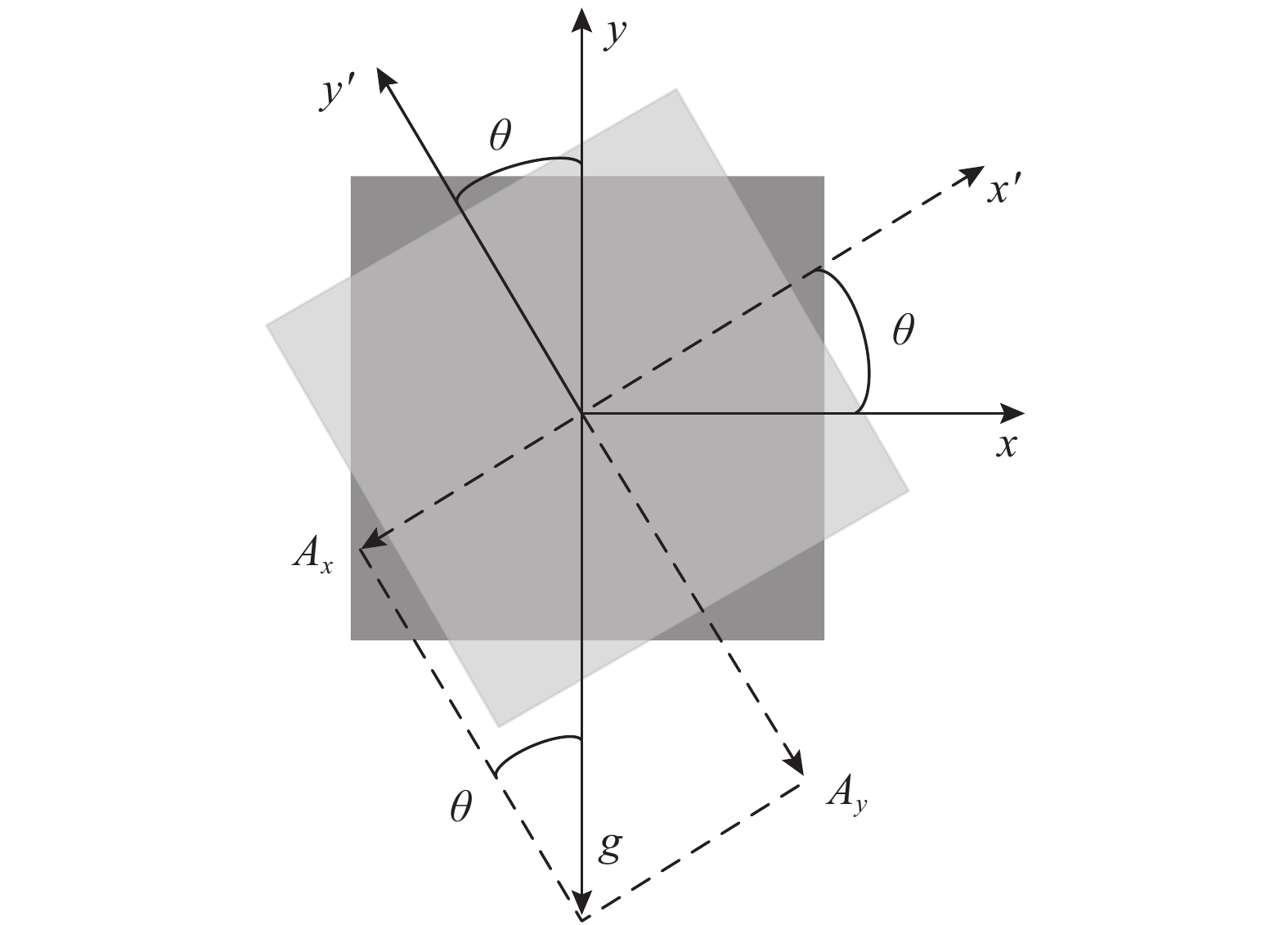
 下载:
下载: