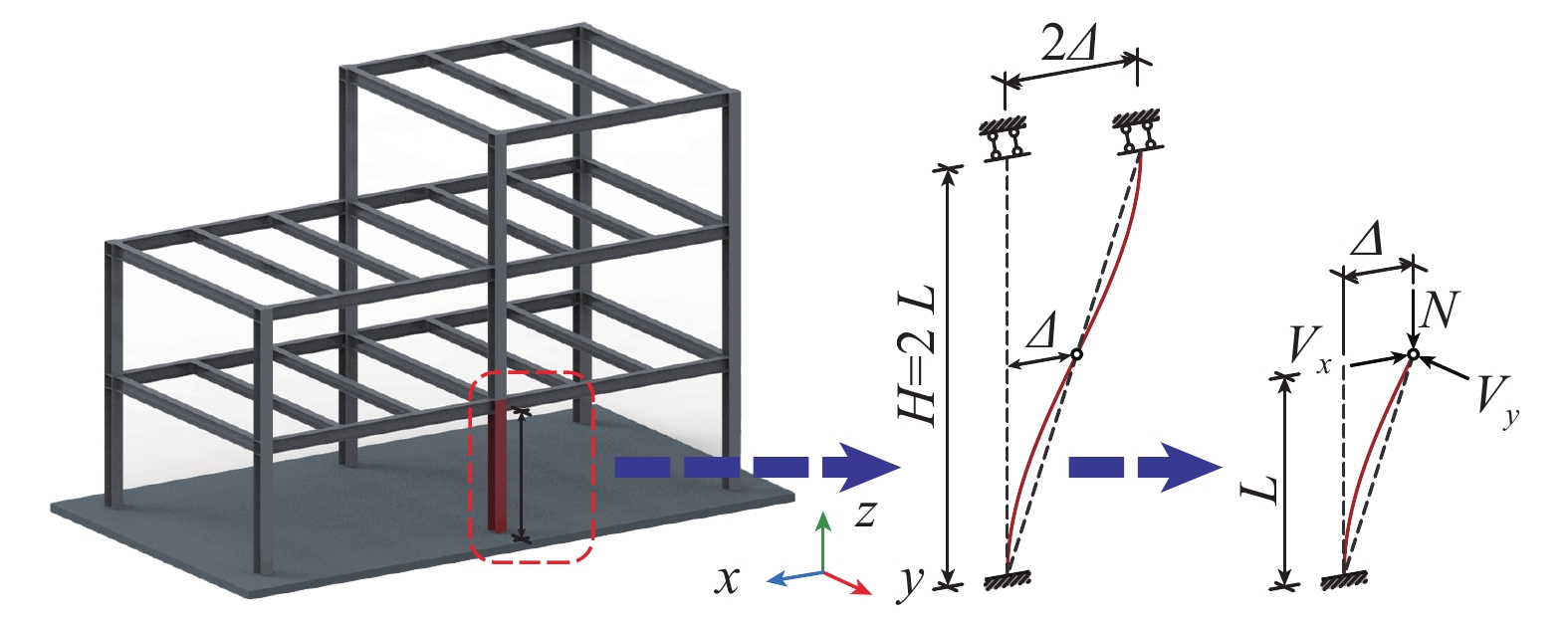
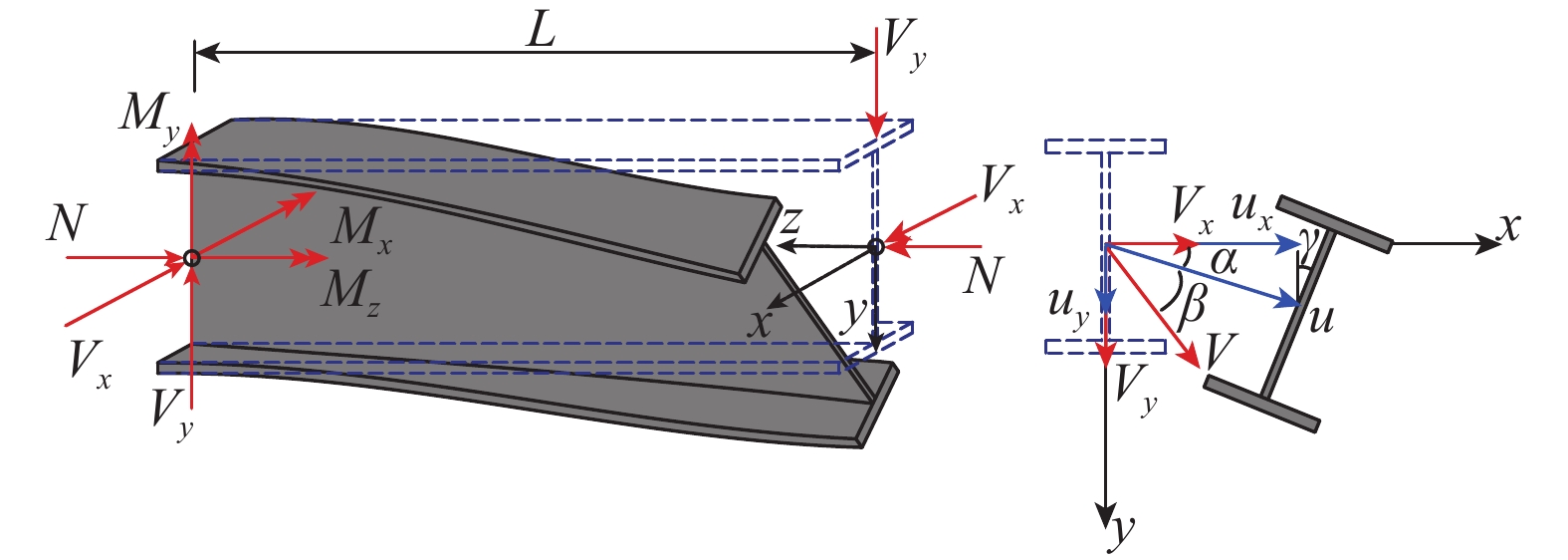
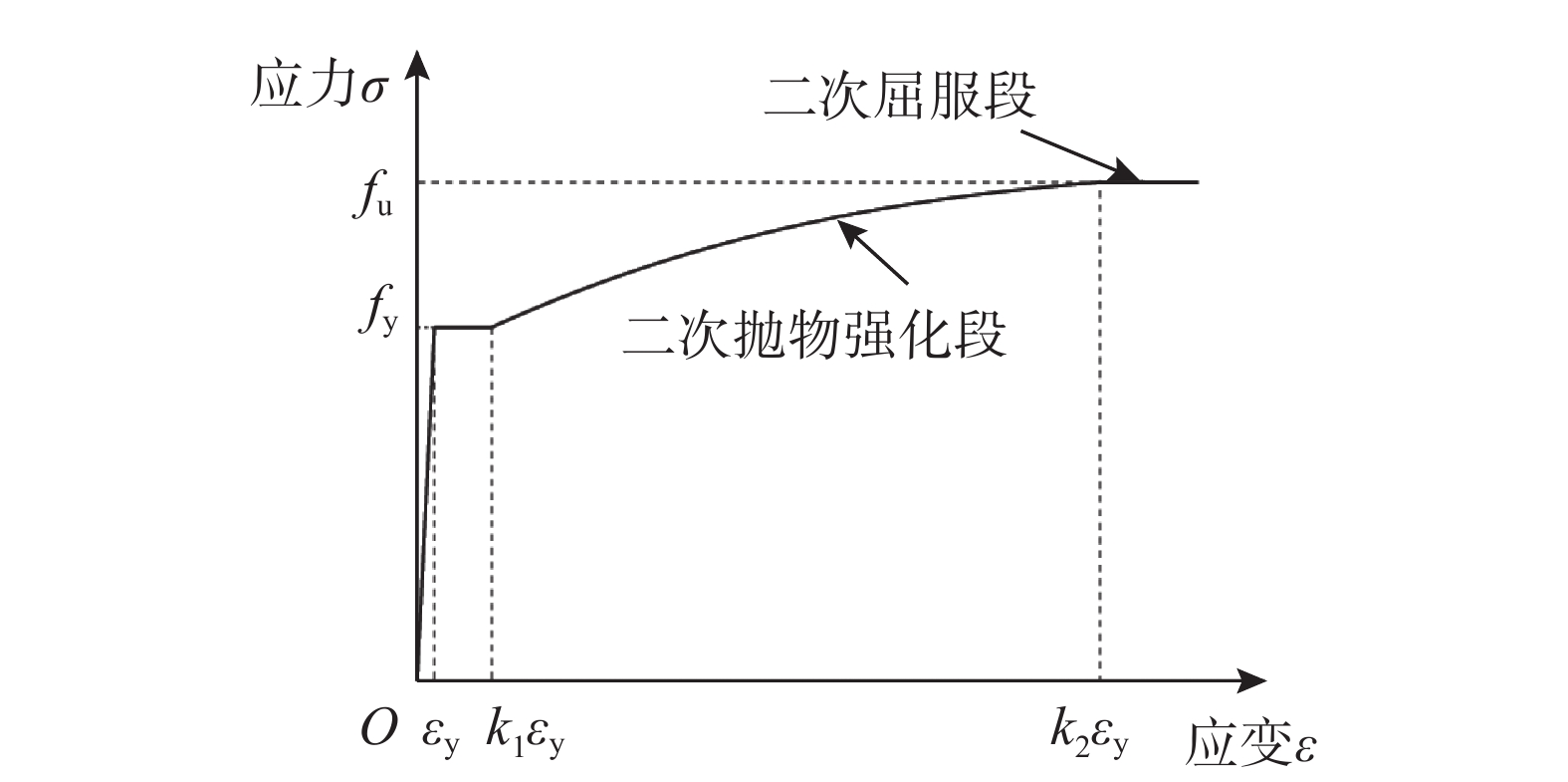
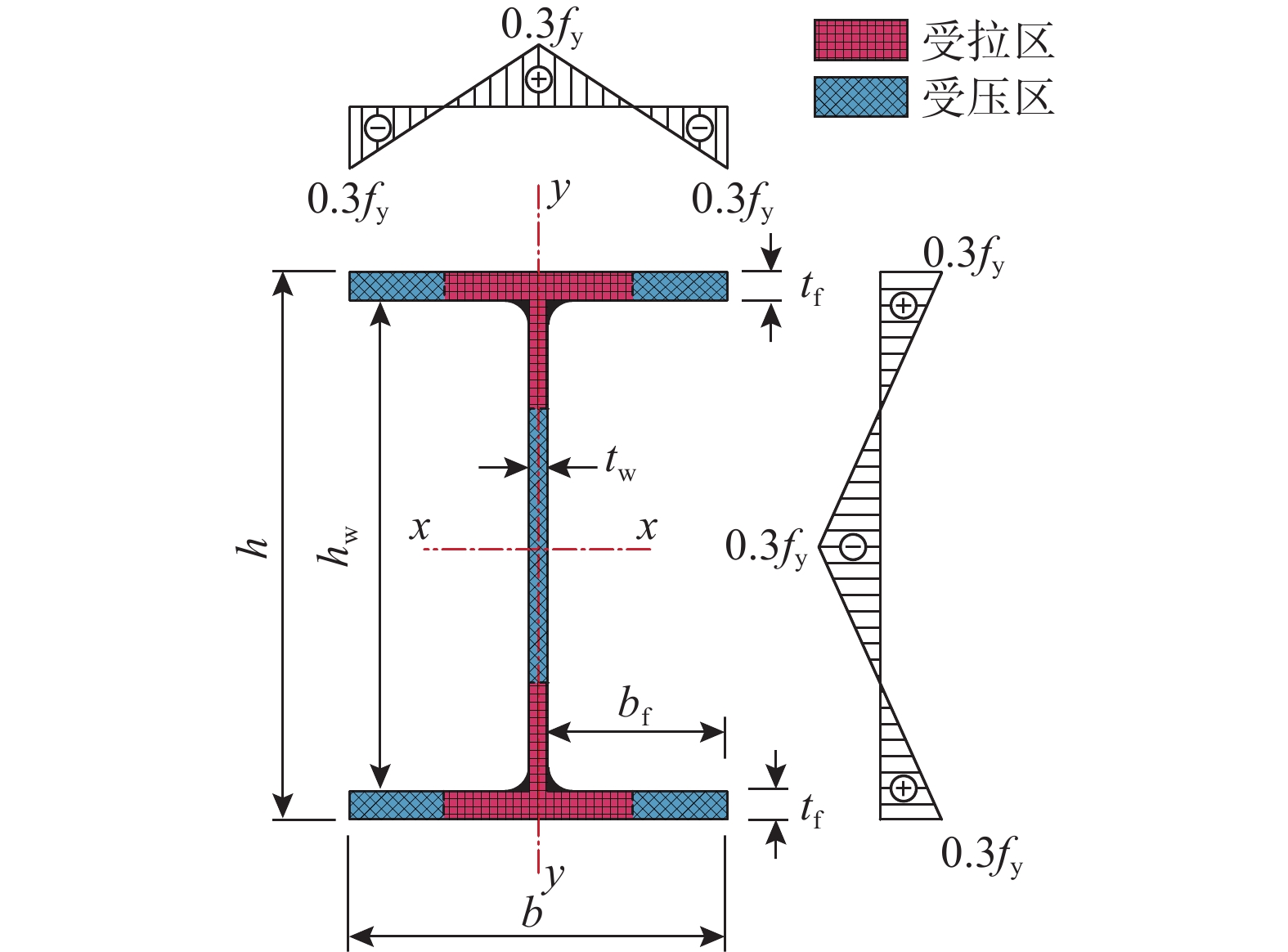
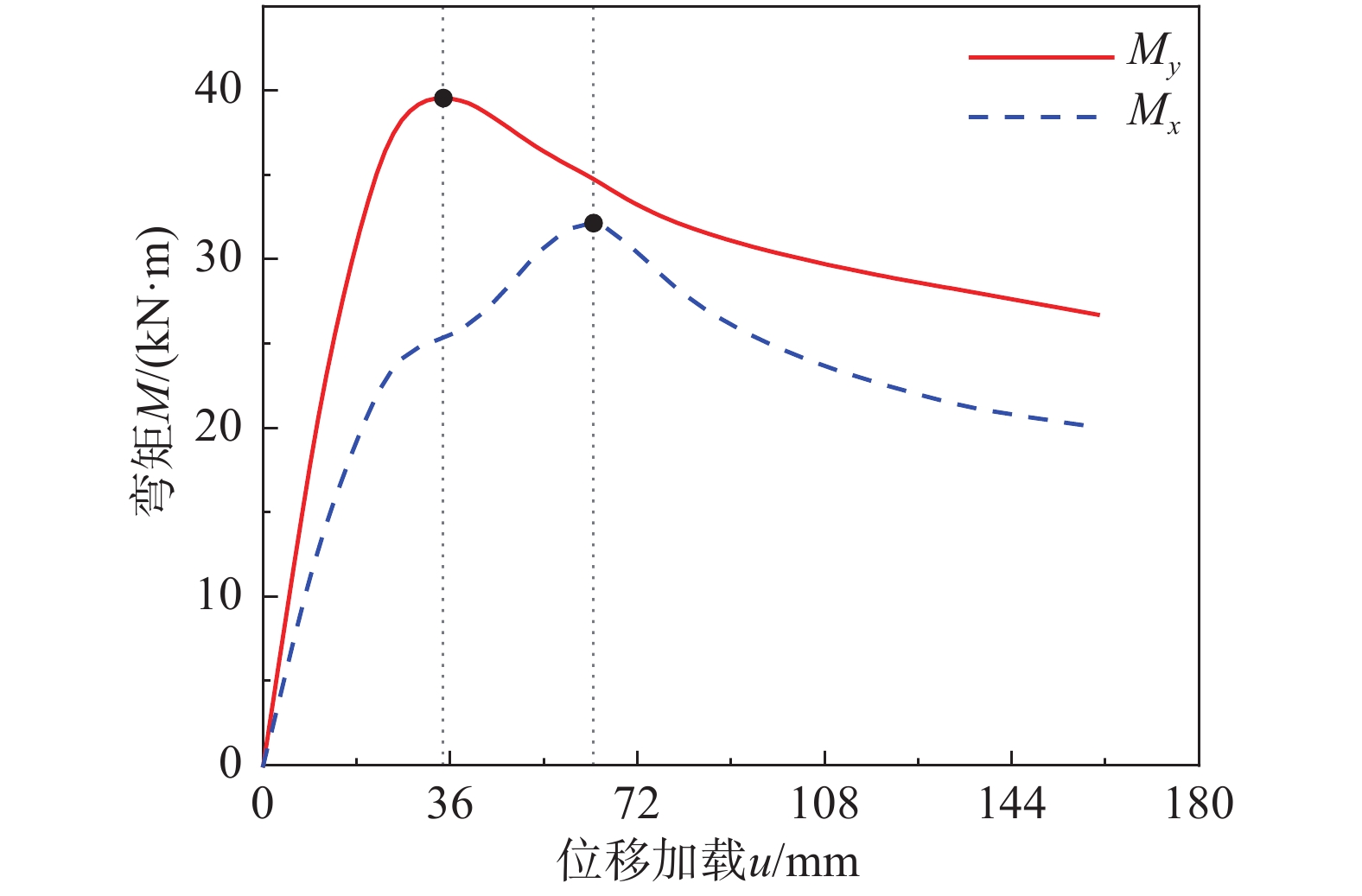
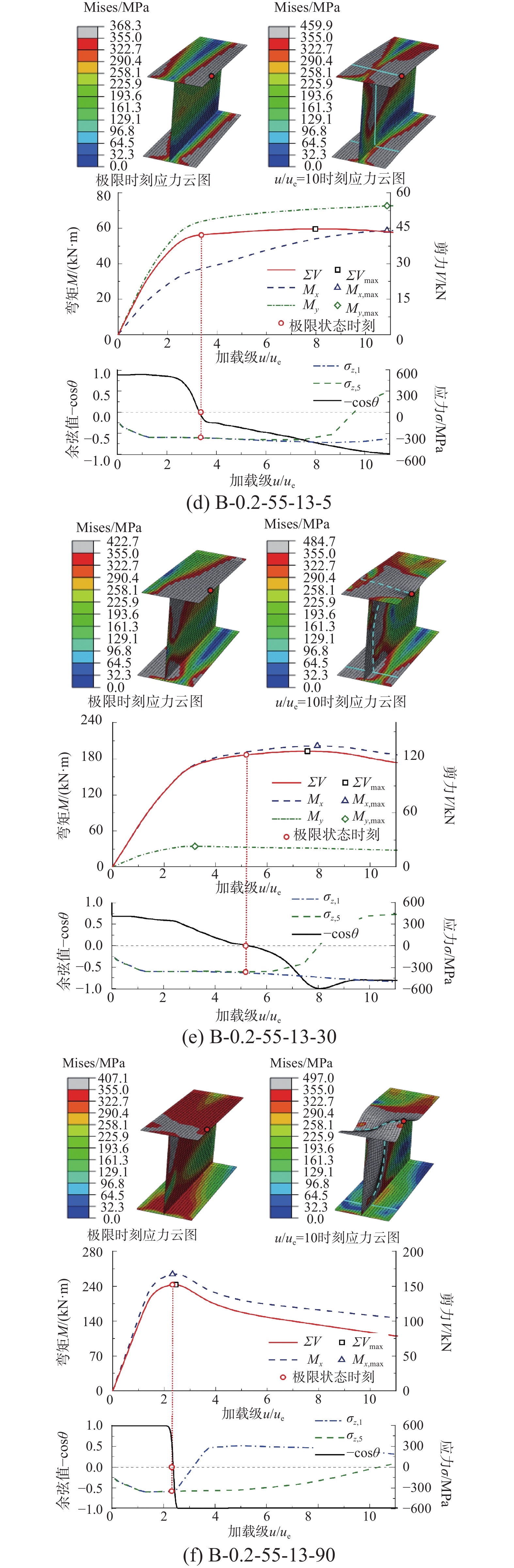
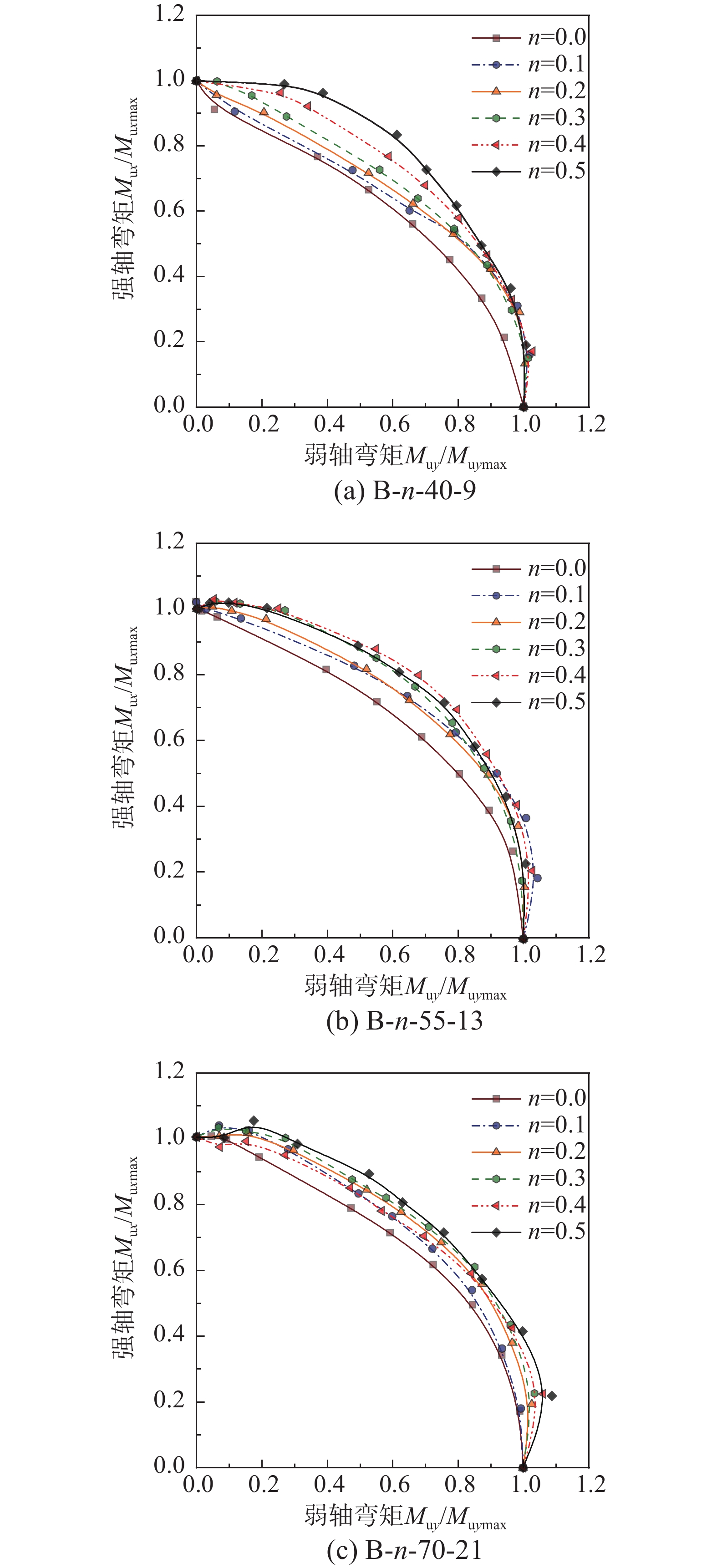
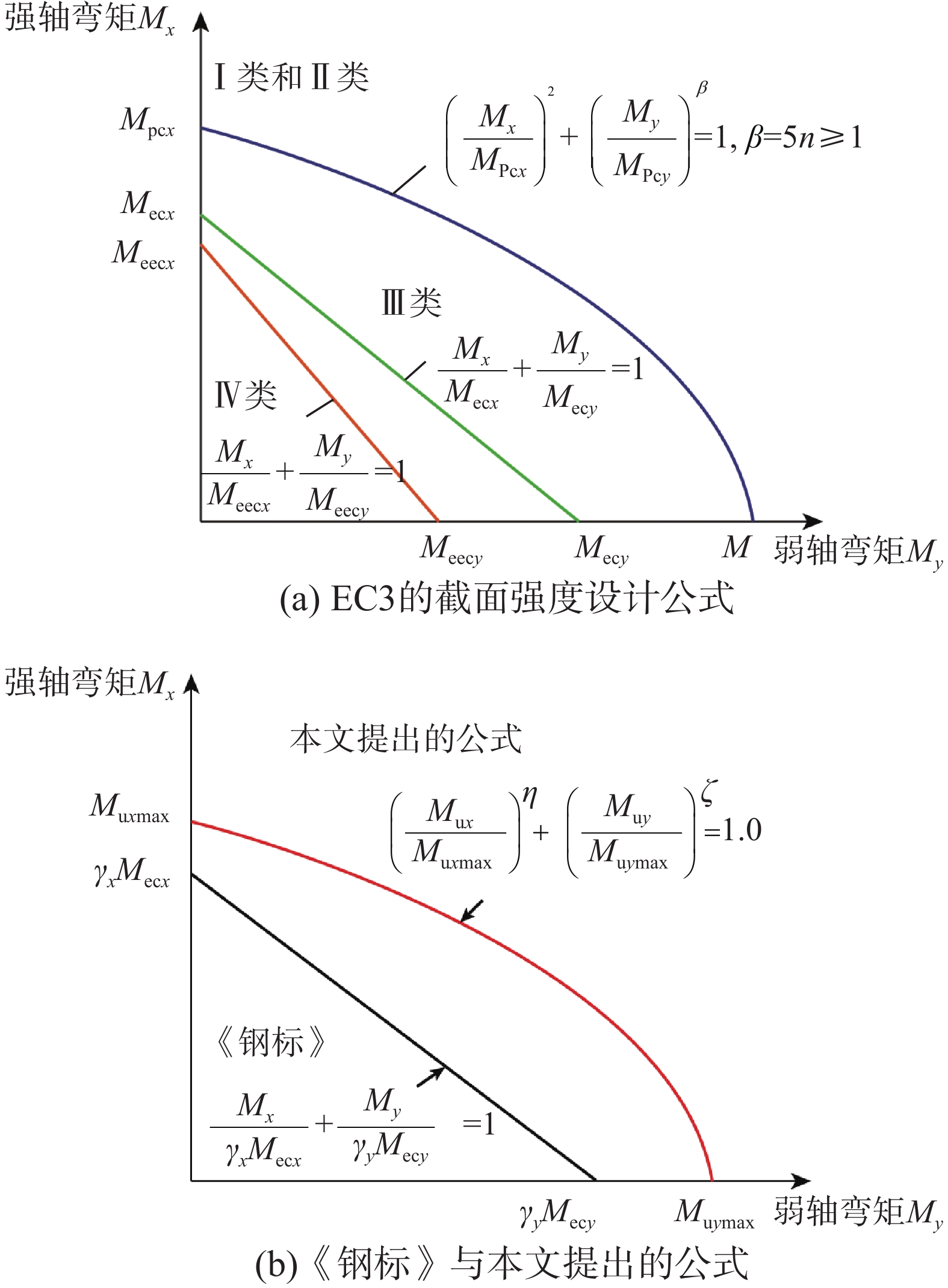
STUDY ON ULTIMATE BEARING CAPACITY OF BIAXIAL COMPRESSION-BENDING STEEL MEMBERS WITH THIN AND SLENDER H-SHAPED SECTION
-
摘要: 为探究薄柔H形截面双向压弯构件的极限状态性能,采用ABAQUS建立了不同轴压比、腹板和翼缘宽厚比的H形截面构件在不同加载角度下的参数分析模型,分析中考虑了材料非线性、几何非线性及残余应力的影响,并基于已有试验数据验证了该模型的适用性。基于经典弹塑性稳定理论,提出了用于确定双向压弯构件极限状态的判定准则,对于塑性铰截面定义为截面出现塑性铰时达到其极限状态;对于由局部屈曲控制的薄柔截面其极限状态为屈曲起始时刻,且该准则能够准确识别出板件局部屈曲的发生。通过最小二乘法拟合得到双轴弯矩极限相关曲线,呈现出腹板和翼缘宽厚比及轴压力的复杂相关影响关系。提出了考虑材料的强化作用和板件相关作用的极限相关计算公式,能够良好地预测H形截面双向压弯构件的极限承载力,且不受截面分类的限制,具有良好的适用性。Abstract: To investigate the ultimate behavior of H-section members with large width-thickness ratios under a combined biaxial compression-bending, the parametric analysis models of H-section members with different axial force ratios, web and flange width-thickness ratios and different loading angles were developed by ABAQUS. Material and geometric nonlinearity were considered throughout the whole analysis, and the finite element models were validated by previous laboratory test results. Based on the elastic-plastic stability theory, a criterion for determining the ultimate state of biaxial compression-bending members was proposed. For plastic-hinge sections, the ultimate state is defined as the occurrence of plastic hinge. For slender sections controlled by local buckling, the ultimate state is the initial buckling moment, with the occurrence of plate local buckling been accurately identified through the criterion. The ultimate interactive curves of biaxial bending moments were obtained by least-square method, within which complicated interactive effects of width-thickness ratios of web and flange and the axial force were noted. The ultimate interactive formula for biaxial moments considering the strain hardening effect of material and the correlation effect of plate was proposed. Not limited by section classification, the proposed method is proved to have good applicability and accuracy.
-
-
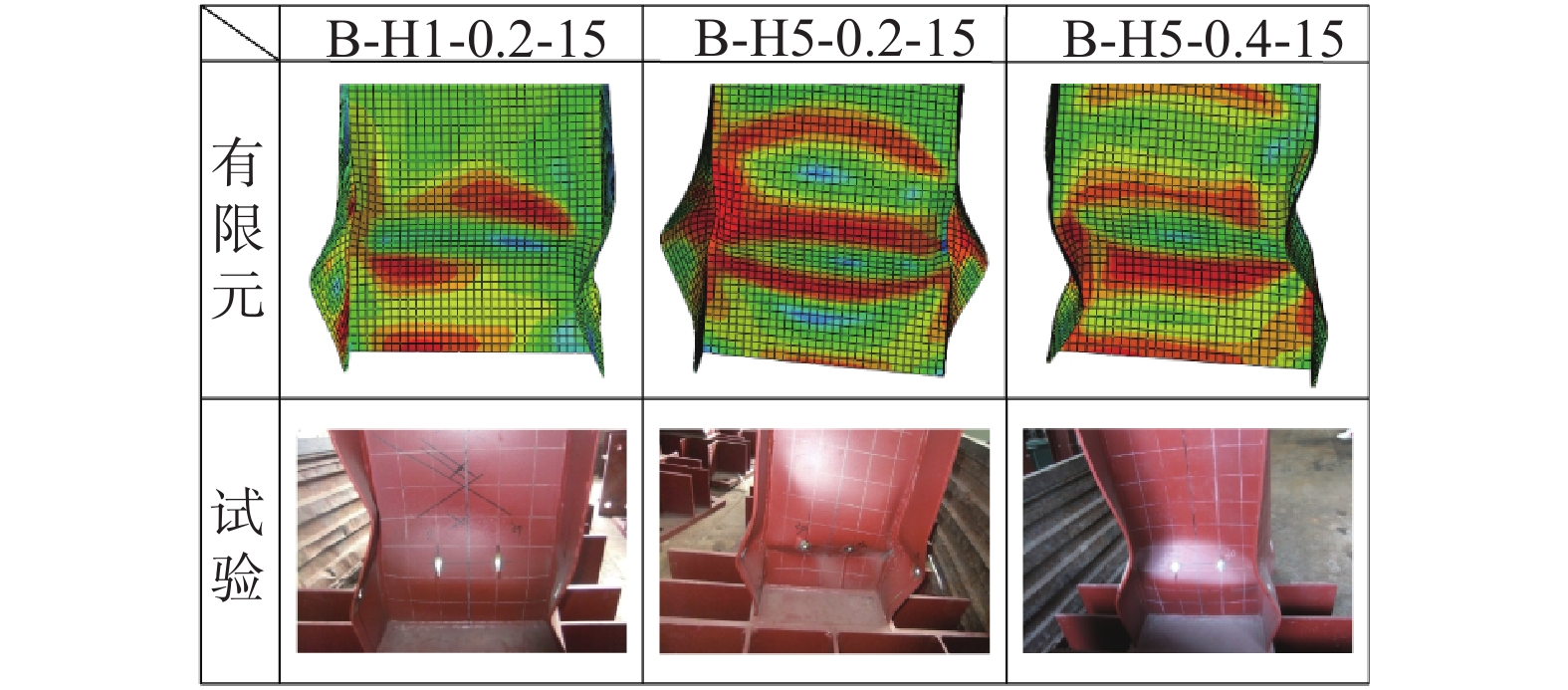
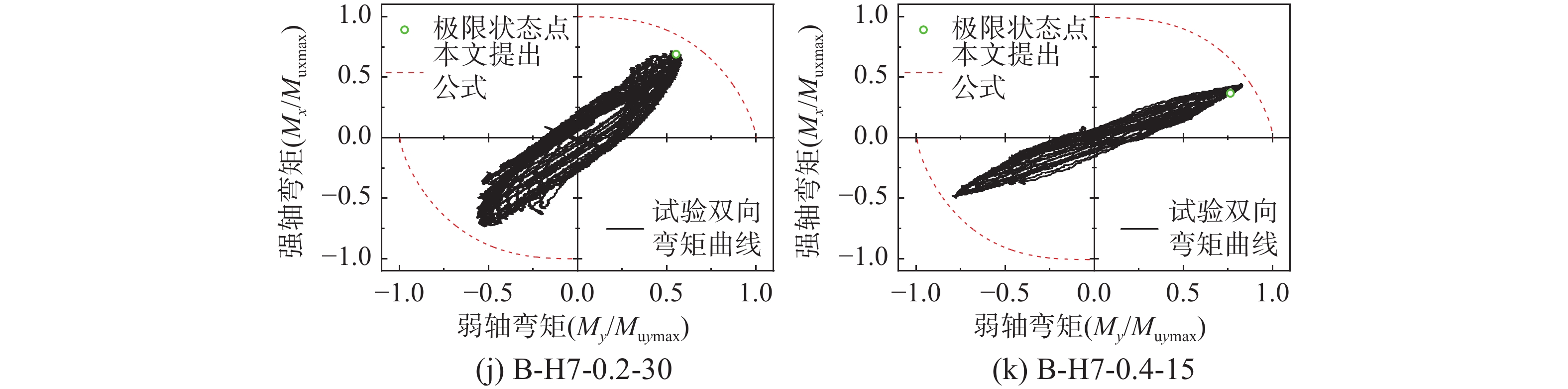
表 1 有限元结果与试验结果[21]比较
Table 1 Comparison between finite element results and available experimental results[21]
试件编号 rw rf Mxmax,test/
(kN·m)Mxmax,FEA/
(kN·m)Mxmax,test/
Mxmax,FEAMymax,test/
(kN·m)Mymax,FEA/
(kN·m)Mymax,test/
Mymax,FEAB-H1-0.2-15 61 35 61.9 63.5 0.975 19.0 20.2 0.941 B-H2-0.2-15 117 16 79.9 87.2 0.916 20.8 20.4 1.020 B-H3-0.2-15 118 30 54.1 60.6 0.893 13.2 13.5 0.978 B-H3-0.2-30 64.5 60.9 1.059 10.2 10.2 1.000 B-H4-0.2-15 117 21 77.8 79.8 0.975 35.7 32.7 1.092 B-H4-0.2-30 103.8 94.7 1.096 26.3 27.1 0.970 B-H5-0.2-15 100 21 74.4 61.1 1.218 35.3 35.1 1.006 B-H5-0.4-15 44.8 50.2 0.892 32.9 33.1 0.994 B-H6-0.2-15 100 16 66.3 74.2 0.894 20.8 18.5 1.124 B-H7-0.2-30 42 11 130.8 128.3 1.019 30.7 27.6 1.112 B-H7-0.4-15 69.1 73.3 0.943 41.9 38.6 1.085 平均值 0.989 1.029 标准差/(%) 9.780 6.010 注:rw=hw/tw√fy/235,rf=bf/tf√fy/235;Mxmax,test和Mymax,test分别为试验结果的强轴和弱轴弯矩分量的峰值;Mxmax,FEA和Mymax,FEA分别为有限元结果的强轴和弱轴弯矩分量的峰值。 表 2 参数设置范围
Table 2 Range of parameter values
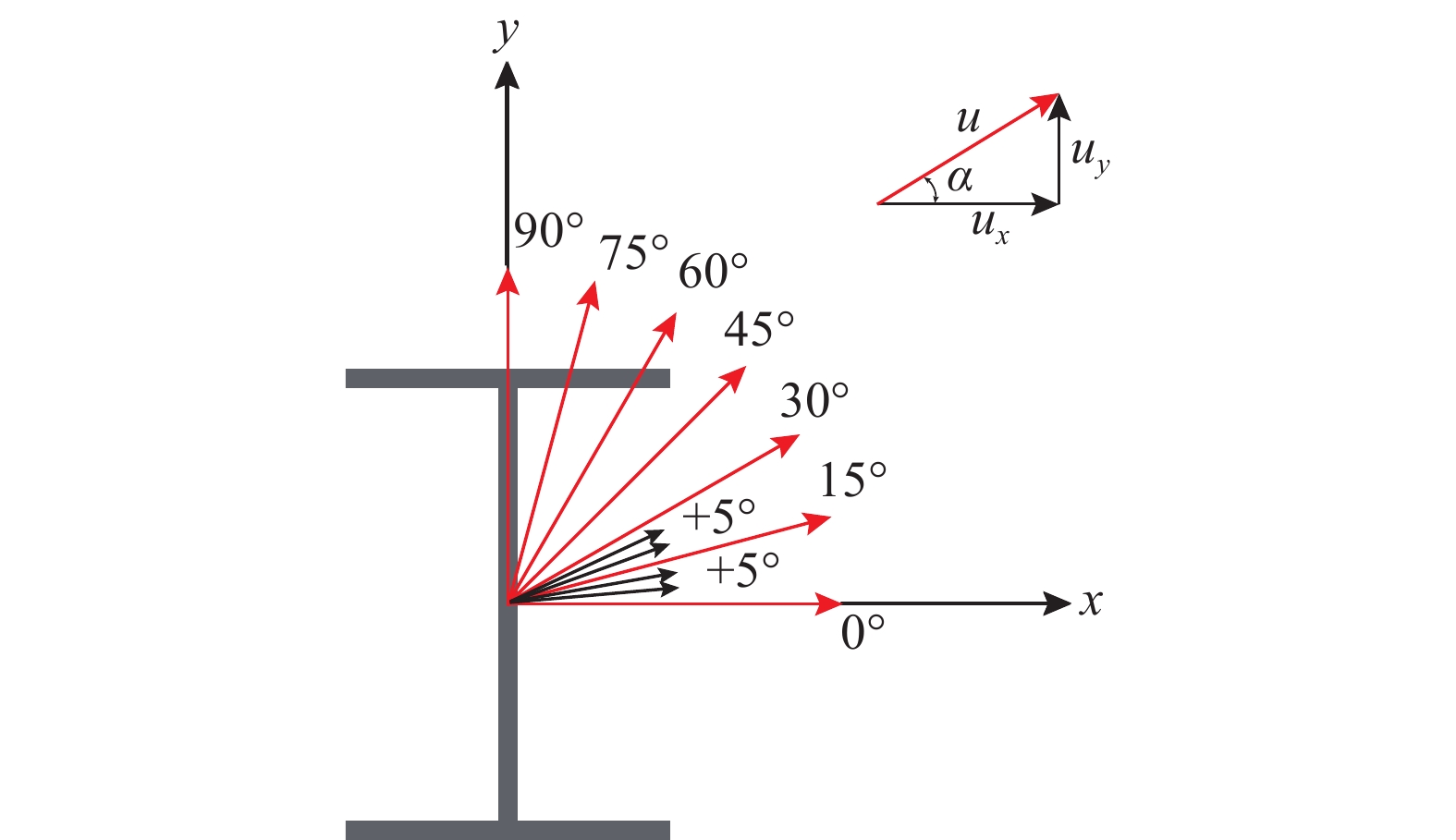
关键参数 参数值 n 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5 rw 40, 55, 70, 85, 100, 115, 130 rf 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21 α/(°) 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90 表 3 可靠度分析结果
Table 3 Reliability analysis results
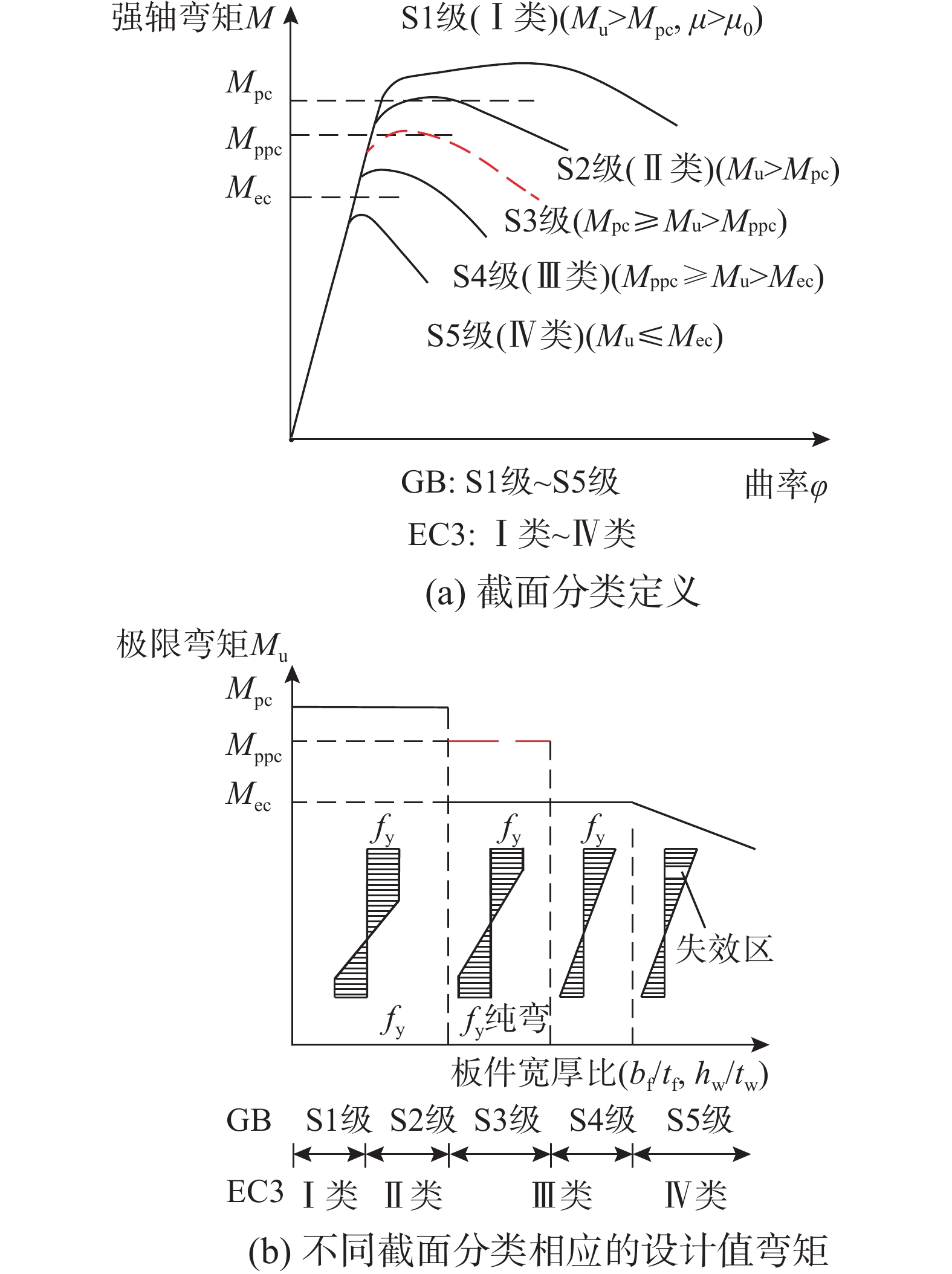
截面分类 Ru,EC3/Ru,FEM Ru,proposed/Ru,FEM 平均值 标准差/(%) 平均值 标准差/(%) I和II类 0.66 10.32 1.01 4.43 III类 0.56 13.69 0.98 4.94 IV类 0.47 14.60 0.97 7.48 I~IV类 0.50 14.97 0.98 6.99 -
[1] 陈以一, 王伟, 童乐为, 等. 装配式钢结构住宅建筑的技术研发和市场培育[J]. 住宅产业, 2012(12): 32 − 35. Chen Yiyi, Wang Wei, Tong Lewei, et al. Technology Development and Market Cultivation of Prefabricated Steel Structure Residential Building [J]. Housing Industry, 2012(12): 32 − 35. (in Chinese)
[2] Yong C X, Zhong P T. Comparative study on the design schemes of residential steel structure [J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2012, 2080: 581 − 584.
[3] 王萌, 柯小刚, 吴照章. 可更换延性耗能连接组件的钢框架节点抗震性能研究[J]. 工程力学, 2018, 35(12): 151 − 163. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2017.09.0743 Wang Meng, Ke Xiaogang, Wu Zhaozhang. Seismic behavior of steel frame connections with replaceable high ductility and energy dissipation components [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2018, 35(12): 151 − 163. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2017.09.0743
[4] CEN. Eurocode 3: Design of steel structures - Part 1-1: General rules and rules for buildings [S]. Brussels, CEN/TC250, 2005.
[5] GB 50017−2017, 钢结构设计规范[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2017. GB 50017−2017, Design code for steel structures [S]. Perking: China Planning Press, 2017. (in Chinese)
[6] 陈乐川, 程欣, 陈以一. 考虑局部屈曲的H形截面钢构件单轴压弯恢复力模型研究[J]. 工程力学, 2021, 38(4): 80 − 92. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2020.05.0326 Chen Lechuan, Cheng Xin, Chen Yiyi. Research on restoring force model of h-section steel members under uniaxial compression and bending considering local buckling [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2021, 38(4): 80 − 92. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2020.05.0326
[7] 程欣, 侯雪松, 李卓峰. 考虑板件相关作用的H形截面分类准则[J]. 工程力学, 2020, 37(4): 178 − 185. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2019.05.0266 Cheng Xin, Hou Xuesong, Li Zhuofeng. Cross-section classification criteria of steel h-sections considering theplate interaction effect [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2020, 37(4): 178 − 185. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2019.05.0266
[8] Watanabe E, Sugiura K, Oyawa W O. Effects of multi-directional displacement paths on the cyclic behaviour of rectangular hollow steel columns [J]. Japan Society of Civil Engineers, 2000(647): 79 − 95.
[9] Guerrero N, Marante M E, Picón R, et al. Model of local buckling in steel hollow structural elements subjected to biaxial bending [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2006, 63(6): 779 − 790.
[10] 申红侠. 高强钢焊接薄壁箱形截面双向压弯构件的稳定承载力[J]. 建筑钢结构进展, 2020, 22(4): 57 − 67. Shen Hongxia. The stability of high-strength steel welded thin-walled box beam-columns under biaxial bending [J]. Progress in Steel Building Structures, 2020, 22(4): 57 − 67. (in Chinese)
[11] Goto Y, Muraki M, Obata M. Ultimate state of thin-walled circular steel columns under bidirectional seismic accelerations [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2009, 135(12): 1481 − 1490. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0000076
[12] Goto Y, Ebisawa T, Lu X, et al. Ultimate state of thin-walled circular steel columns subjected to biaxial horizontal forces and biaxial bending moments caused by bidirectional seismic accelerations [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2014, 4(141): 4014122-1 − 4014122-12.
[13] 范峰, 聂桂波, 支旭东, 等. 圆钢管空间滞回试验及材料本构模型[J]. 土木工程学报, 2011, 44(12): 18 − 24. Fan Feng, Nie Guibo, Zhi Xudong, et al. Spatial hysteresis experiment and constitutive model for circular steel pipes [J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2011, 44(12): 18 − 24. (in Chinese)
[14] Zubydan A H. Inelastic large deflection analysis of space steel frames including H-shaped cross sectional members [J]. Engineering Structures, 2013, 48: 155 − 165. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2012.09.024
[15] Baptista A M. Resistance of steel I-sections under axial force and biaxial bending [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2012, 72: 1 − 11. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2011.07.013
[16] Cheng X, Chen Y. Ultimate strength of H-sections under combined compression and uniaxial bending considering plate interaction [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2018, 143: 196 − 207. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2017.12.019
[17] Cheng X, Chen Y, Nethercot D A. Experimental study on H-shaped steel beam-columns with large width-thickness ratios under cyclic bending about weak-axis [J]. Engineering Structures, 2013, 49: 264 − 274. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2012.10.035
[18] Cheng X, Chen Y, Pan L. Experimental study on steel beam–columns composed of slender H-sections under cyclic bending [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2013, 88: 279 − 288. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2013.05.020
[19] Yun X, Gardner L, Boissonnade N. Ultimate capacity of I-sections under combined loading – Part 1: Experiments and FE model validation [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2018, 147: 408 − 421. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2018.04.016
[20] Yun X, Gardner L, Boissonnade N. Ultimate capacity of I-sections under combined loading – Part 2: Parametric studies and CSM design [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2018, 148: 265 − 274. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2018.05.024
[21] Cheng X, Chen Y, Niu L, et al. Experimental study on H-section steel beam-columns under cyclic biaxial bending considering the effect of local buckling [J]. Engineering Structures, 2018, 174: 826 − 839. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2018.08.001
[22] 石永久, 王萌, 王元清. 结构钢材循环荷载下的本构模型研究[J]. 工程力学, 2012, 29(9): 92 − 98. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2010.09.0711 Shi Yongjiu, Wang Meng, Wang Yuanqing. Study on constitutive model of structural steel under cyclic loading [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2012, 29(9): 92 − 98. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2010.09.0711
[23] ECCS. Ultimate limit state calculation of sway frames with rigid joints [M]. Brussels (Belgium): ECCS General Secretariat, 1984.
[24] 胡世光, 梁炳文. 弹塑性稳定理论[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1983. Hu Shiguang, Liang Bingwen. Elastic plastic stability theory [M]. Peking: National Defense Industry Press, 1983. (in Chinese)
[25] Hill R. A general theory of uniqueness and stability in elastic-plastic solids [J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 1958, 3(6): 236 − 249.
[26] Bresler B. Design criteria for reinforced columns under axial load and biaxial bending [J]. Journal Proceedings, 1960, 57(11): 481 − 490.
[27] Mohammad A, Ashraf M, Ahmed S. Behaviour and design of stainless steel slender cross-sections subjected to combined loading [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2016, 104: 225 − 237. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2016.03.020
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 梁刚,陈江,李淑敏,卢俊龙. 梁柱节点弯剪型可更换耗能件抗震性能数值分析. 地震工程与工程振动. 2025(02): 173-182 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李晓梦,韩灵杰. 冲击荷载下建筑用钢梁摩擦摇摆柱节点的抗震性能. 兵器材料科学与工程. 2025(03): 91-96 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: