EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON FAILURE MODES OF COMPRESSION MEMBERS IN SPACE STRUCTURES STRENGTHENED WITH SLEEVES
-
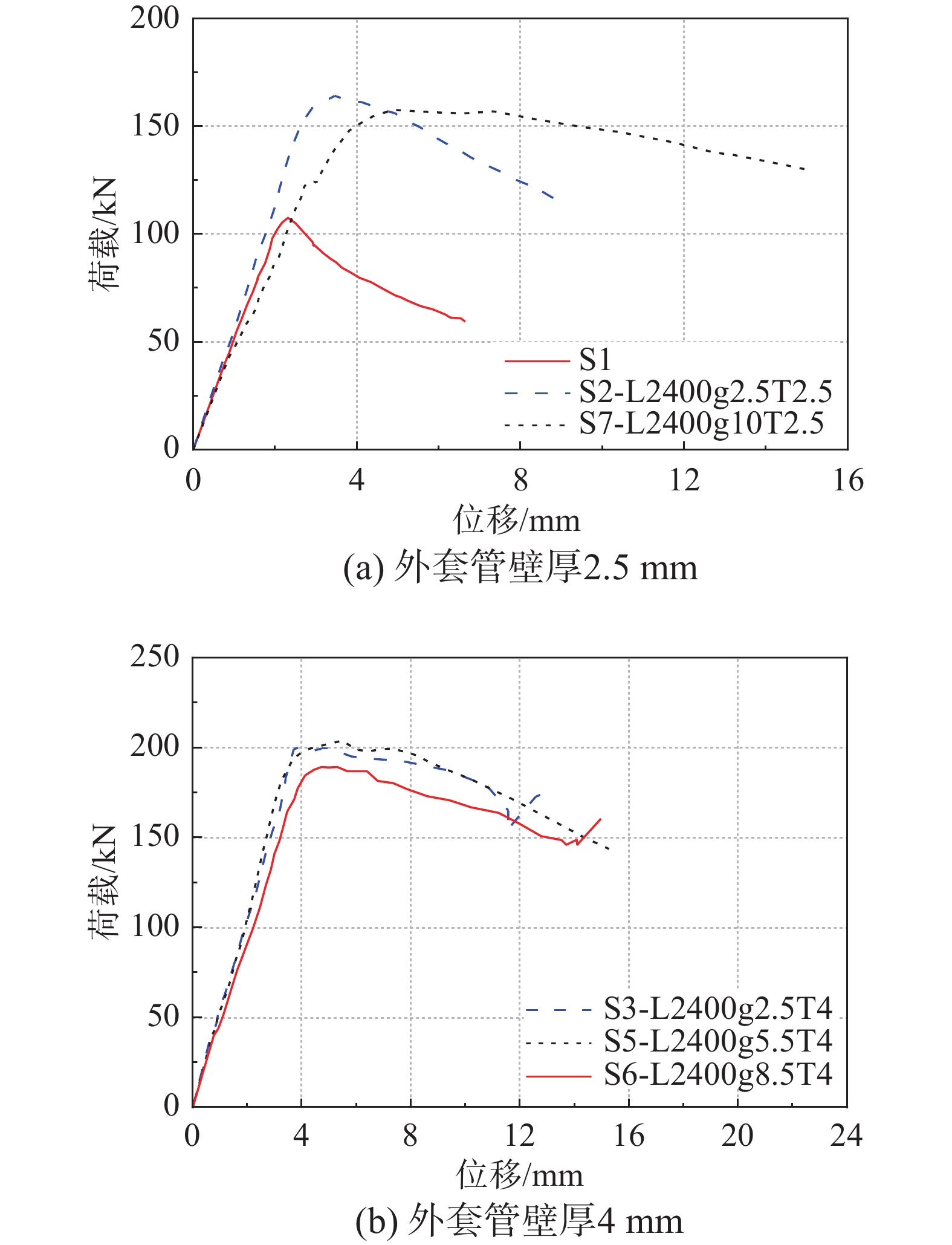
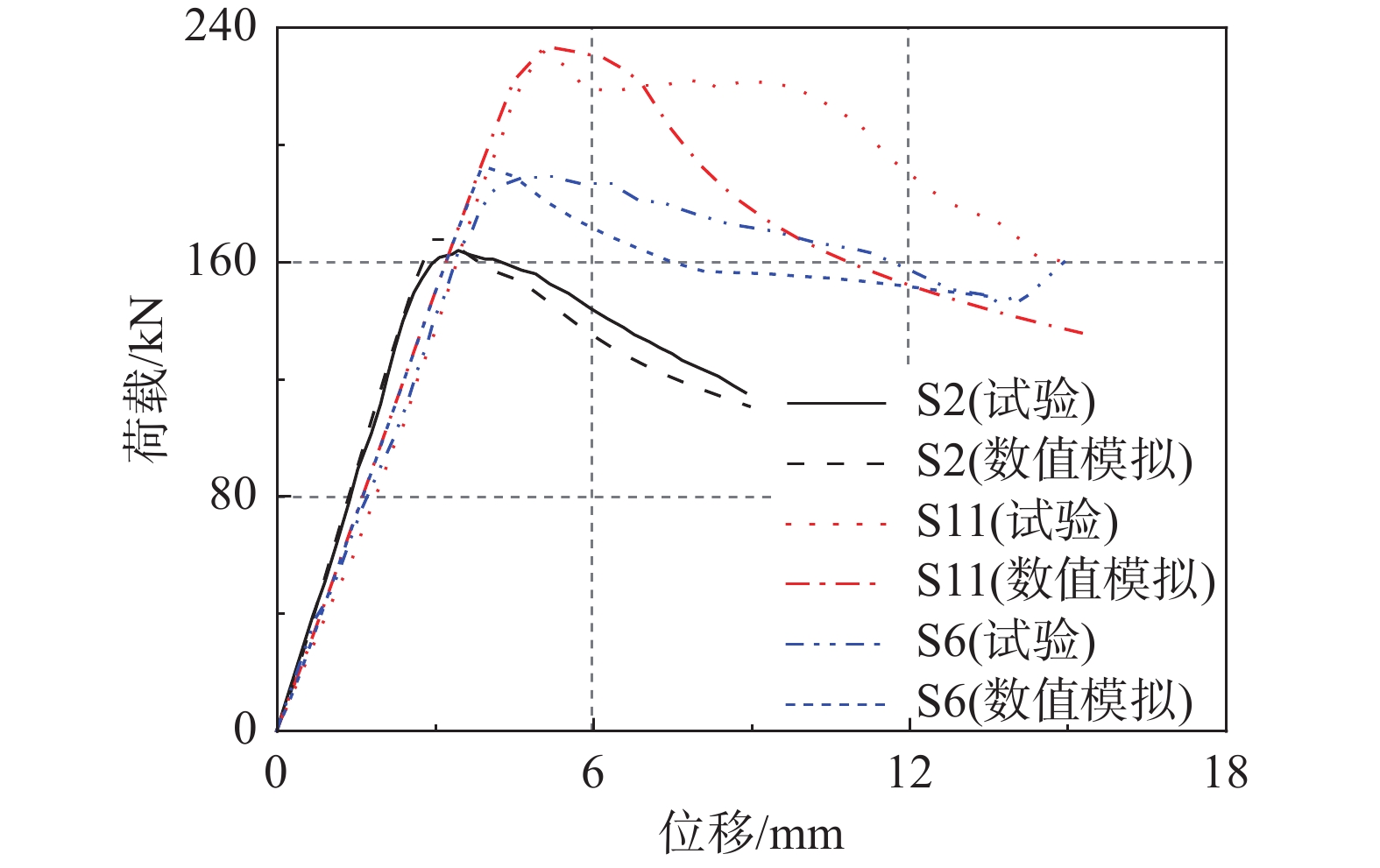
摘要: 空间结构压杆失稳是结构失效的重要原因之一。利用套管加固空间结构压杆以抑制压杆屈曲,增加构件的极限承载能力和延性。通过对不同壁厚、套管与内压杆间隙和内压杆外伸段长度的12根试件进行轴压试验,得到加固前后试件的极限承载能力、破坏模式和延性变化。加固后试件的极限承载能力最大提高了147%,且外套管壁厚越大,内压杆外伸段越短,承载力越高;内压杆与外套管间隙越大,承载力略有下降。加固试验中构件的破坏模式由加固前的整体屈曲失稳变化为加固后的整体失稳、内压杆端部外伸段失稳和两种耦合失稳,且壁厚越小,易发生整体失稳,外伸段越长,易发生内压杆端部失稳,间隙对失稳形态影响不明显。此外,加固后试件延性均大于未经加固内压杆,经过合理设计延性指标能够增加一倍以上。Abstract: The Instability of compression members of space structures is one of the important causes of structural failure. The sleeves were applied to reinforce the compression members in space structures to restrain the buckling of the compression members, and to improve the ultimate bearing capacity and the ductility of the components. Thusly, axial compression tests were conducted on 12 specimens to investigate the ultimate bearing capacity, the failure modes and, the ductility of the compression members with and without sleeves. Key parameters include the sleeves thickness, the gap between the inner compression members and sleeves, and the overhang length of the inner compression members. The maximum increment for the ultimate bearing capacity of the specimens after reinforcing was 146%. Besides, the bearing capacity increased with the increase of the sleeves thickness and, with the decrease of the overhang length of the inner compression members. The bearing capacity decreased slightly with the gap between the inner compression members and the sleeves. After reinforcing the compression members, the failure modes of the components changed from the overall instability of the compression members to the coupling instability of compression members and their inner overhangs. Moreover, the overall instability was prone to occur with the decrease of the sleeves thickness. The instability of the overhang of the inner compression members was likely to be observed with the overhang length. The influence of gap on the failure modes was not obvious. In addition, the ductility of all specimens with sleeves is larger than that of the specimens without sleeves, and the ductility index could be more than doubled with reasonable design.
-
Keywords:
- space structure /
- compression member /
- sleeve reinforcement /
- failure mode /
- ultimate bearing capacity /
- ductility
-
-
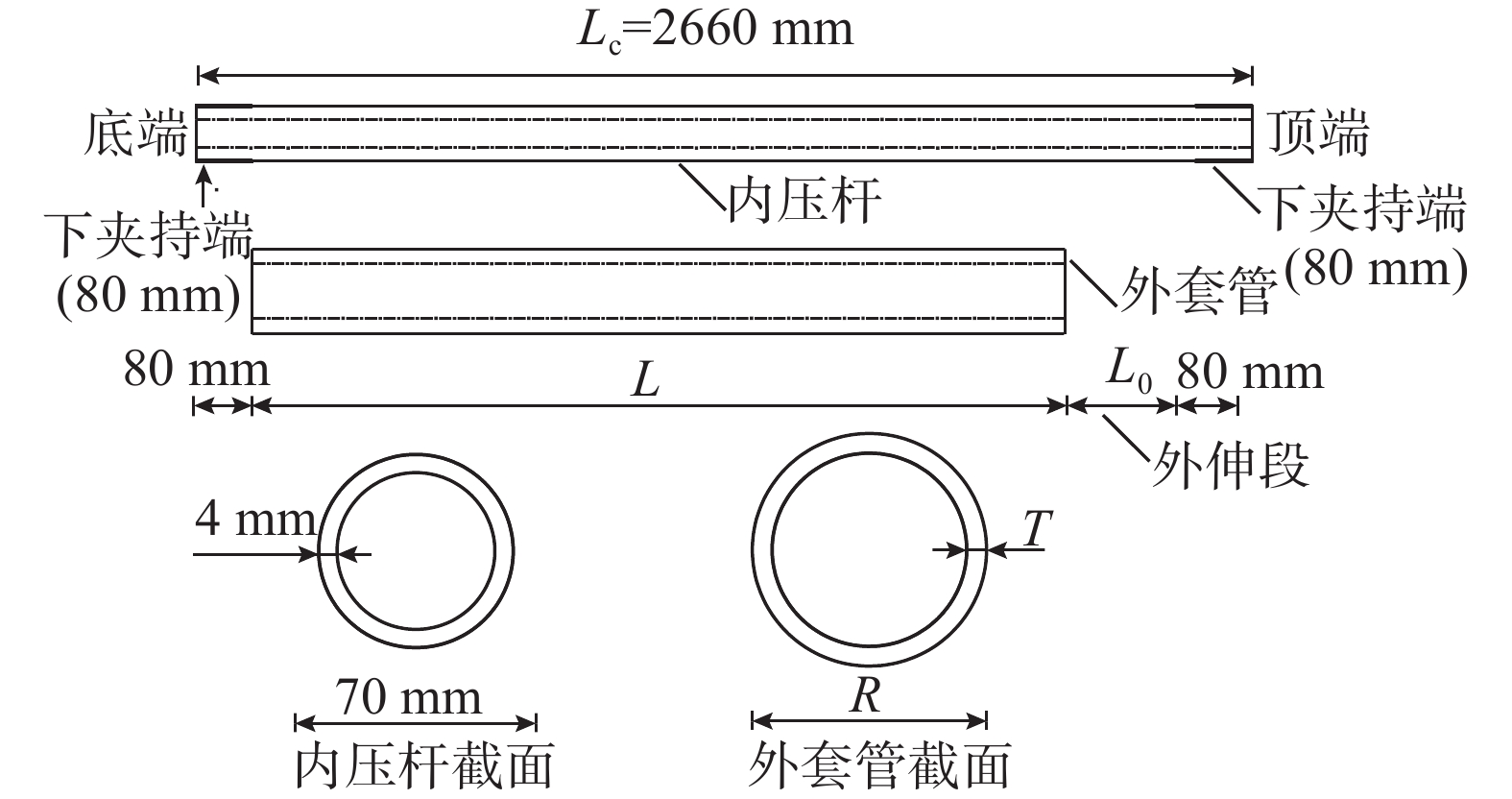
表 1 套管设计尺寸
Table 1 Design values of sleeves
/mm 试件号 试件名 外套管
总长度L外套管
外径R外套管
壁厚T内压杆外伸
端长度L0间隙值g S2 L2400g2.5T2.5 2400 80 2.5 100 2.5 S3 L2400g2.5T4 83 4 2.5 S4 L2400g2.5T10 95 10 2.5 S5 L2400g5.5T4 89 4 5.5 S6 L2400g8.5T4 95 4 8.5 S7 L2400g10T2.5 95 2.5 10 S8 L2400g2.5T6 87 6 2.5 S9 L2350g2.5T6 2350 87 6 150 2.5 S10 L2450g2.5T6 2450 87 6 50 2.5 S11 L2450g2.5T4 83 4 2.5 S12 L2450g2.5T10 95 10 2.5 注:L、R和T分别为外套管总长度、外径和壁厚;L0为内压杆外伸端长度;g为外套管与内压杆之间间隙值,为外套管内径与内压杆外径差值的一半。 表 2 试件实测尺寸
Table 2 Measured values of specimens
/mm 试件号 外套管
总长度L外套管
外径R外套管
壁厚T内压杆外伸
端长度L0间隙值g S1* 2660.53 69.86 4.26 − − S2 2400.17 80.05 2.68 100.00 2.34 S3 2397.60 83.56 4.32 103.40 2.61 S4 2398.90 96.23 10.93 100.63 2.23 S5 2397.87 88.95 4.18 103.70 5.26 S6 2399.13 94.80 4.31 101.93 8.09 S7 2399.07 94.86 2.54 100.93 9.89 S8 2389.67 89.02 6.36 101.40 3.24 S9 2350.07 89.42 6.52 151.47 3.24 S10 2451.20 89.23 6.48 48.83 3.19 S11 2451.43 83.44 4.55 49.57 2.23 S12 2449.40 95.40 10.92 51.33 1.90 注:S1*行中为所有试件的内压杆实测尺寸平均值。 表 3 材料性能参数
Table 3 Material constants
试样 弹性模量E/GPa 名义屈服强度σ0.2/MPa 抗拉极限强度σb/MPa 断后伸长率δ/(%) R70T4 190.87 303.98 462.05 21.04 R80T2.5 206.51 327.56 488.04 19.66 R83T4 193.03 310.89 476.52 18.81 R89T4 203.62 336.56 465.94 24.33 R87T6 195.55 276.02 451.10 21.42 R95T2.5 206.34 342.03 471.09 19.61 R95T4 205.08 276.38 459.85 21.17 R95T10 209.44 314.93 476.22 18.17 注:R为试件外径尺寸;T为试件壁厚。 表 4 试件试验结果
Table 4 Test results of specimens
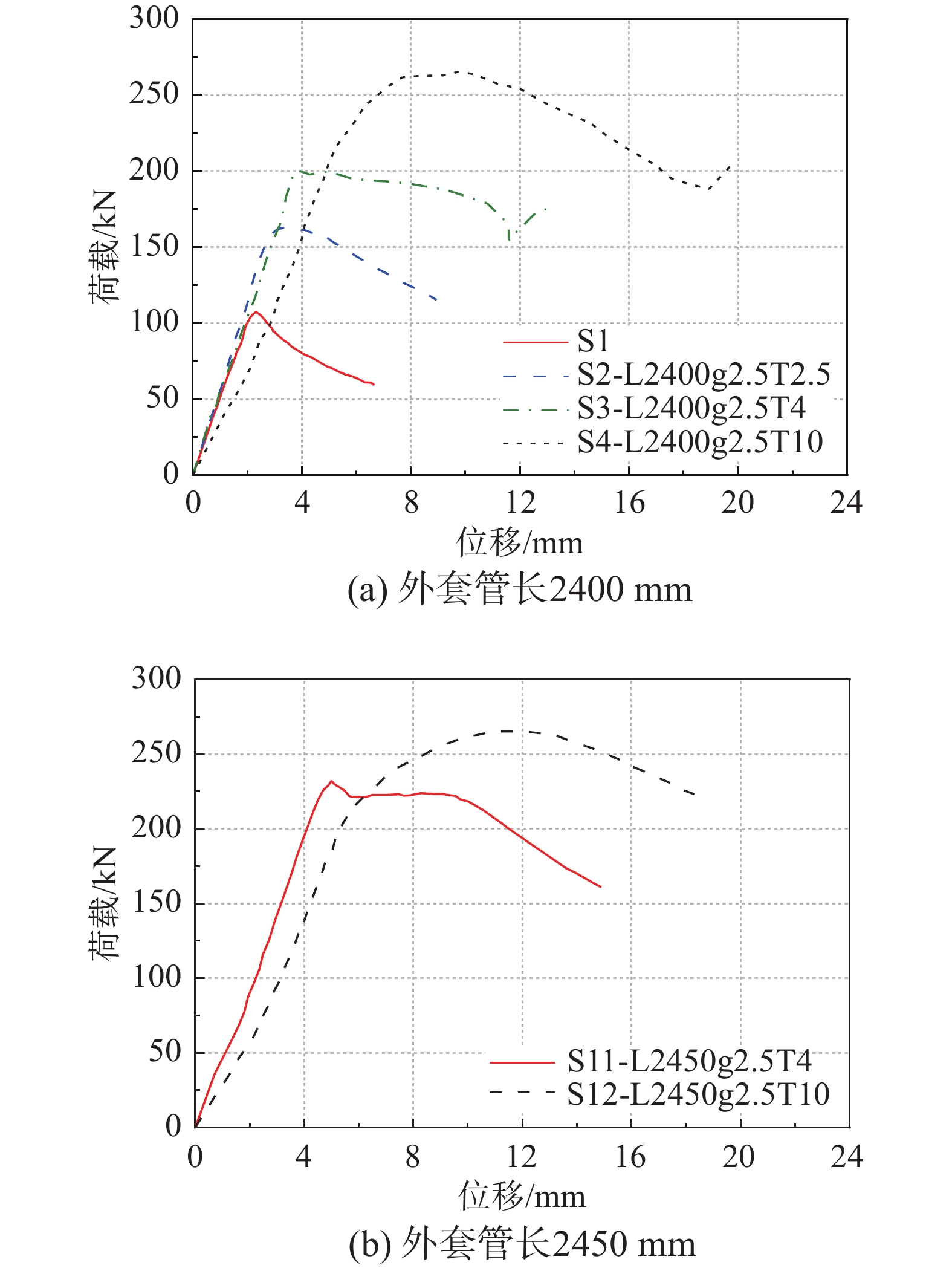
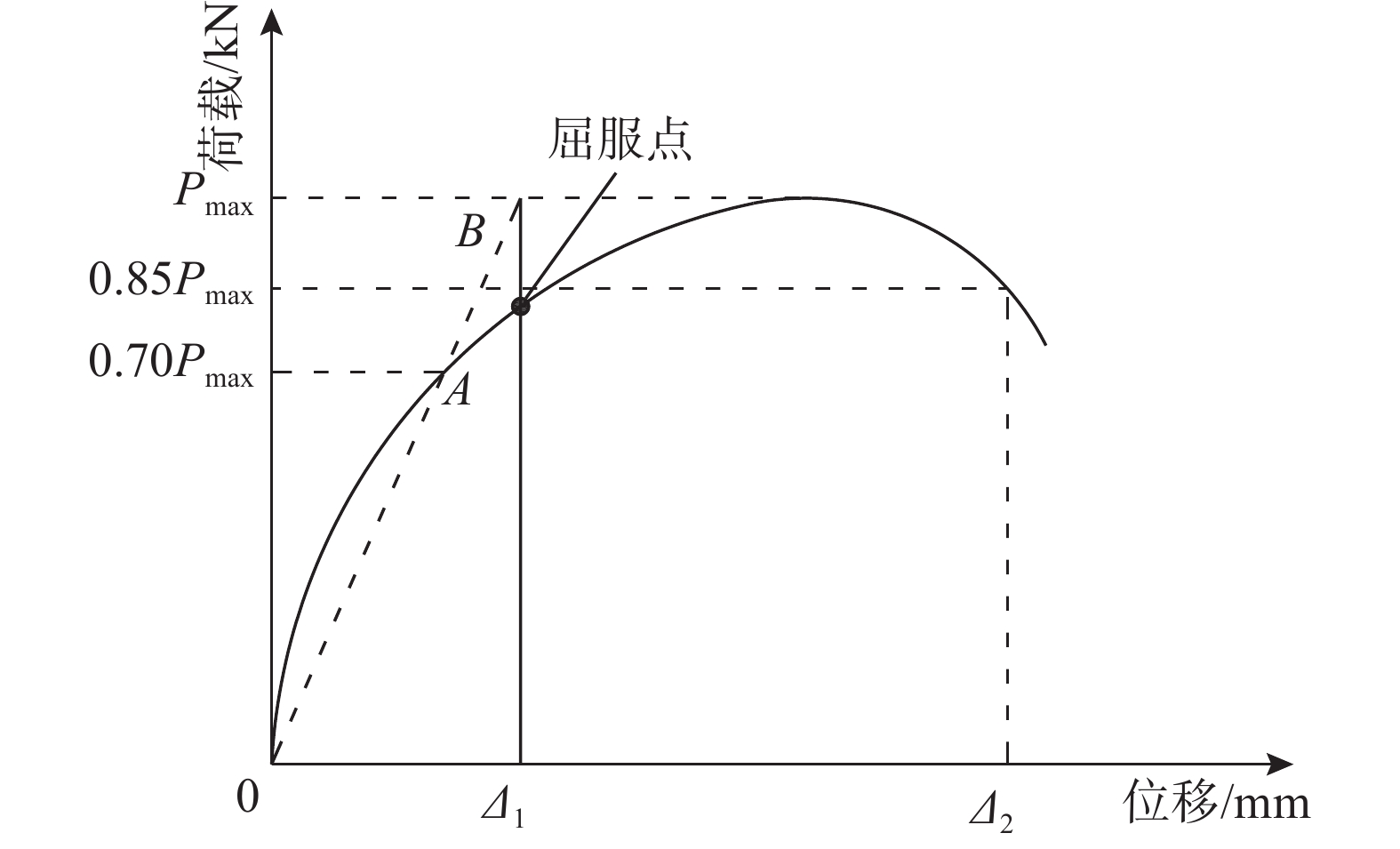
试件号 试件名 试件峰值承载力Pmax/kN 试件延性指标u S1 − 107.54 1.67 S2 L2400g2.5T2.5 164.13 2.55 S3 L2400g2.5T4 200.13 3.04 S4 L2400g2.5T10 265.34 2.07 S5 L2400g5.5T4 203.85 2.12 S6 L2400g8.5T4 189.23 3.95 S7 L2400g10T2.5 157.54 3.22 S8 L2400g2.5T6 227.69 4.28 S9 L2350g2.5T6 214.15 2.71 S10 L2450g2.5T6 220.00 1.82 S11 L2450g2.5T4 232.15 3.45 S12 L2450g2.5T10 260.22 2.35 注:Pmax为试件峰值承载力;u为试件的延性指标,相关讨论见3.3节。 表 5 试件破坏模式
Table 5 Failure modes of specimens
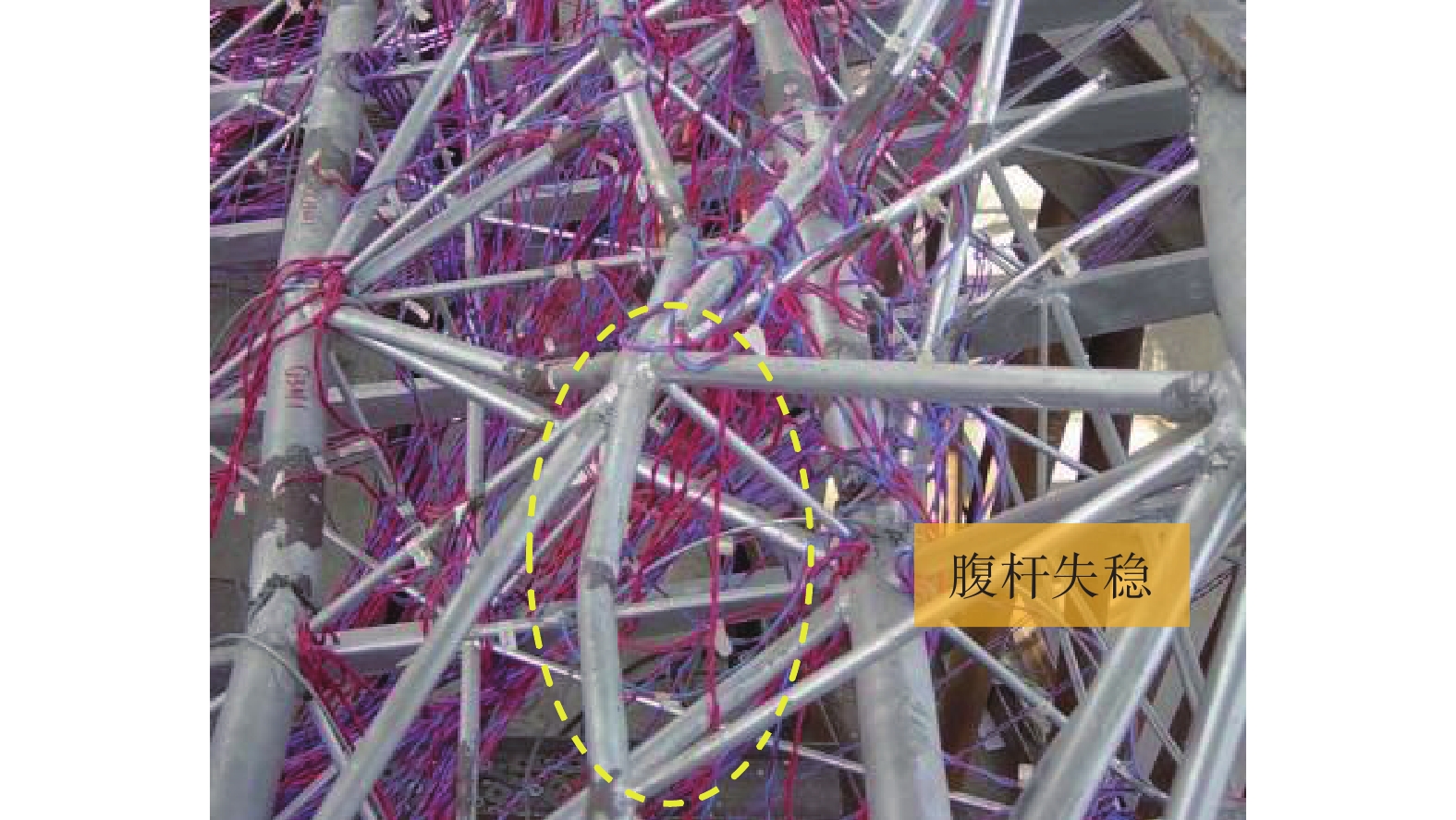
试件 S1 S2 S3 S4 整体形态 



端部形态 



模式 整体失稳 整体失稳 端部失稳 端部失稳 试件 S5 S6 S7 S8 整体形态 



端部形态 



模式 耦合失稳 端部失稳 整体失稳 端部失稳 试件 S9 S10 S11 S12 整体形态 



破坏形态 



模式 端部失稳 端部失稳 耦合失稳 端部失稳 -
[1] 赵宪忠, 闫伸, 陈以一. 大跨度空间结构连续性倒塌研究方法与现状[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2013, 34(4): 1 − 14. doi: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2013.04.015 ZHAO Xianzhong, YAN Shen, CHEN Yiyi. A review on progressive collapse study for large-span space structures [J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2013, 34(4): 1 − 14. (in Chinese) doi: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2013.04.015
[2] MURTHA-SMITH E. Alternate path analysis of space trusses for progressive collapse [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1988, 114(9): 1978 − 1999. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1988)114:9(1978)
[3] ABEDI K, PARKE G A R. Progressive collapse of single-layer braced domes [J]. International Journal of Space Structures, 1996, 11(3): 291 − 306. doi: 10.1177/026635119601100302
[4] BHOWMICK A K, GRONDIN G Y. Limit state design of steel columns reinforced with welded steel plates [J]. Engineering Structures, 2016, 114(2): 48 − 60.
[5] 王元清, 宗亮, 施刚, 等. 钢结构加固新技术及其应用研究[J]. 工业建筑, 2017, 47(2): 1 − 6, 22. doi: 10.13204/j.gyjz201702001 WANG Yuanqing, ZONG Liang, SHI Gang, et al. Application research on new strengthing technologies for steel structures [J]. Industrial Construction, 2017, 47(2): 1 − 6, 22. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13204/j.gyjz201702001
[6] ZHAO X L, ZHANG L. State-of-the-art review on FRP strengthened steel structures [J]. Engineering Structures, 2007, 29(11): 1808 − 23.
[7] 黄波, 陈泉, 李涛, 等. 国标Q235钢屈曲约束支撑低周疲劳试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2013, 46(6): 29 − 34, 43. doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2013.06.010 HUANG Bo, CHEN Quan, LI Tao, et al. Low-cycle fatigue test of Q235 steel buckling-restrained braces [J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2013, 46(6): 29 − 34, 43. (in Chinese) doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2013.06.010
[8] WANG C L, USAMI T, FUNAYAMA J, et al. Low-cycle fatigue testing of extruded aluminium alloy bucklingrestrained braces [J]. Engineering Structures, 2013, 46(9): 294 − 301.
[9] 朱博莉, 郭彦林. 梭形空间桁架约束型防屈曲支撑的性能研究[J]. 工程力学, 2020, 37(7): 35 − 46. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2019.07.0424 ZHU Boli, GUO Yanlin. Investigation on the performance of spatial-truss confined BRBS with shuttle shape longitudinally [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2020, 37(7): 35 − 46. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2019.07.0424
[10] 高向宇, 李杨龙, 李建勤, 等. 钢支撑动力屈曲致扭机理及BRB减扭机理的研究[J]. 工程力学, 2020, 37(11): 83 − 96, 107. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2019.12.0748 GAO Xiangyu, LI Yanglong, LI Jianqin, et al. Study on the mechanism of torsion induced by steel brace dynamic buckling and the mechanism of torsion reduction supplied by BRB [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2020, 37(11): 83 − 96, 107. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2019.12.0748
[11] 金双双, 李盈开, 周建庭, 等. 全装配式自复位防屈曲支撑滞回模型及其性能试验研究[J]. 工程力学, 2021, 38: 1 − 11. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2020.07.ST04 JIN Shuangshuang, LI Yingkai, ZHOU Jianting, et al. Hysteresis model and experimental investigation of assembled self-centering buckling-restrained braces [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2021, 38: 1 − 11. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2020.07.ST04
[12] 聂祺, 罗开海, 郭浩, 等. 某剧场平板网架屋盖鉴定与修复[J]. 工程抗震与加固改造, 2017, 39(增刊 1): 125 − 130. doi: 10.16226/j.issn.1002-8412.2018.02.019 NIE Qi, LUO Kaihai, GUO Hao, et al. Identification and Reinforcement of A Theater Grid Structure Roof [J]. Earthquake Resistant Engineering and Retrofitting, 2017, 39(Suppl 1): 125 − 130. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16226/j.issn.1002-8412.2018.02.019
[13] SRIDHARA B N. Sleeved compression member [P]. U. S. Patent: 5175972, 1984-7-2.
[14] SRIDHARA B N, RAMASWAMY M A. Sleeved column as compression member [R]. Bangalore, India: Bangalore University, 1982.
[15] PRASAD B K. Experimental investigation of sleeved column [D]. Tucson: University of Arizona, 1989.
[16] 申波. 轴压套管构件静力稳定性能的理论与试验研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学, 2007. SHEN Bo. Theoretical and Experimental Investigations on the Static Stability of Sleeved Compression Members [D]. Shanghai: Tongji University, 2007. (in Chinese)
[17] 胡波. 轴心受压套管构件力学性能精细化分析与试验研究[D]. 浙江: 浙江大学, 2013. HU Bo. Refined analysis on structural behavior and experimental study of axial compressed sleeved member [D]. Zhejiang: Zhejiang University, 2013. (in Chinese)
[18] GB/T 228.1−2010, 金属材料 拉伸试验 第1部分: 室温试验方法[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2010. GB/T 228.1−2010, Metallic materials Tensile testing Part 1: Method of test at room temperature [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2010. (in Chinese)
[19] 张涌泉. 双相型不诱钢轴心受压构件承载力试验研究与理论分析[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2016. ZHANG Yongquan. Theoretical and experimental investigations on the duplex stainless steel axial compression members [D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2016. (in Chinese)
[20] HAN L H, HUANG H, TAO Z, et al. Concrete-filled double skin steel tubular (CFDST) beam–columns subjected to cyclic bending [J]. Engineering Structures, 2006, 28(12): 1698 − 1714. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2006.03.004
[21] 冯鹏, 强翰霖, 叶列平. 材料、构件、结构的“屈服点”定义与讨论[J]. 工程力学, 2017, 34(3): 36 − 46. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2016.03.0192 FENG Peng, QIANG Hanlin, YE Lieping. Discussion and definition on yield points of materials, members and structures [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2017, 34(3): 36 − 46. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2016.03.0192
-
期刊类型引用(22)
1. 李成玉,杨草原,贾良玖,陈焰周. 曲线隅撑和柱端滑移摩擦节点单层钢框架的抗震性能研究. 工程力学. 2025(03): 113-127 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 梁刚,陈江,李淑敏,卢俊龙. 梁柱节点弯剪型可更换耗能件抗震性能数值分析. 地震工程与工程振动. 2025(02): 173-182 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 韩重庆,杨瑞丰,李向民,冷予冰,张富文,许清风. 装配式矩形钢管混凝土柱-钢梁侧板连接节点抗震性能研究. 建筑结构学报. 2024(04): 50-60 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 梁刚,李淑敏,杨佳男,刘云贺,卢俊龙,田庆. 梁柱节点弯剪型可更换耗能件抗震性能试验研究. 工程科学与技术. 2024(05): 221-229 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 韦古强,胡从川,王越,刘广东,翟钱. 装配式混凝土柱脚节点可替换耗能构件抗震性能研究. 甘肃科学学报. 2024(06): 37-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 冯玉龙,韦明途,种迅,蒋庆. 屈曲约束翼缘盖板连接的钢框架节点滞回性能研究. 建筑结构. 2023(05): 110-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 丁发兴,许云龙,王莉萍,尹国安,余志武. 拉筋对两层两跨钢-混凝土组合框架结构抗震性能的影响. 工程力学. 2023(04): 58-70 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 潘建荣,陈鹏,胡方鑫,王湛. 可更换屈曲约束耗能板的钢框架梁柱节点抗震性能试验研究. 建筑结构学报. 2023(S2): 180-187 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 郑宏,苏耀烜,尚永芳,刘智超,江力强. 装配式可更换梁段腹板开孔削弱型节点滞回性能. 建筑科学与工程学报. 2022(01): 25-35 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 乔立强. 关于钢结构建筑中梁柱节点的研究综述. 城市建筑. 2022(16): 175-178 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 杜辉波,程欣,张超,陈以一. 薄柔H形截面双向压弯钢构件极限承载力研究. 工程力学. 2022(09): 191-203 .  本站查看
本站查看
12. 黄炜,胡高兴. 可恢复预制装配式RC梁柱节点抗震性能研究. 工程力学. 2022(12): 165-176+189 .  本站查看
本站查看
13. 李成玉,胡艳平,王军洁,贺东兵,陈焰周. 柱端设置盖板式滑移摩擦节点H型钢柱抗震稳定性研究. 世界地震工程. 2022(04): 83-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 黄彬辉,李元齐. 装配式钢结构梁柱节点承载性能研究进展. 结构工程师. 2021(01): 228-238 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 王凯,王德斌,莫德秀,张皓. 摩擦软钢节点阻尼器抗震及抗倒塌性能. 科学技术与工程. 2021(09): 3733-3739 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. Kim Eng Chouery,樊奎,贾良玖. 对称和非对称型摩擦耗能连接的抗震性能与设计方法研究现状. 工程力学. 2021(05): 22-37+49 .  本站查看
本站查看
17. 叶建峰,郑莲琼,颜桂云,薛潘荣,马永超. 装配式可更换耗能铰滞回性能试验研究. 工程力学. 2021(08): 42-54 .  本站查看
本站查看
18. 杨子仪,叶茂,刘建武,袁金秀. 新型装配式塑性铰节点的设计及数值模拟. 应用力学学报. 2021(04): 1423-1430 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 王萌,孙毅,杨璐. 配置低屈服点角钢连接件的钢框架节点损伤控制及优化设计. 建筑结构学报. 2021(12): 76-89 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 石若利,潘志成,李其伦,谢建斌. 钢框架结构梁柱节点抗震加固有限元分析. 扬州大学学报(自然科学版). 2021(06): 70-78 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 谢鲁齐,吴京,章锦洋,刘晨昱. 可更换耗能连接力学机理及变形性能研究. 工程力学. 2020(06): 186-195 .  本站查看
本站查看
22. 叶冬晨,陈以一. 基于分块组合法的多孔板塑性极限状态分析. 工程力学. 2019(06): 36-48 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(27)




 下载:
下载: